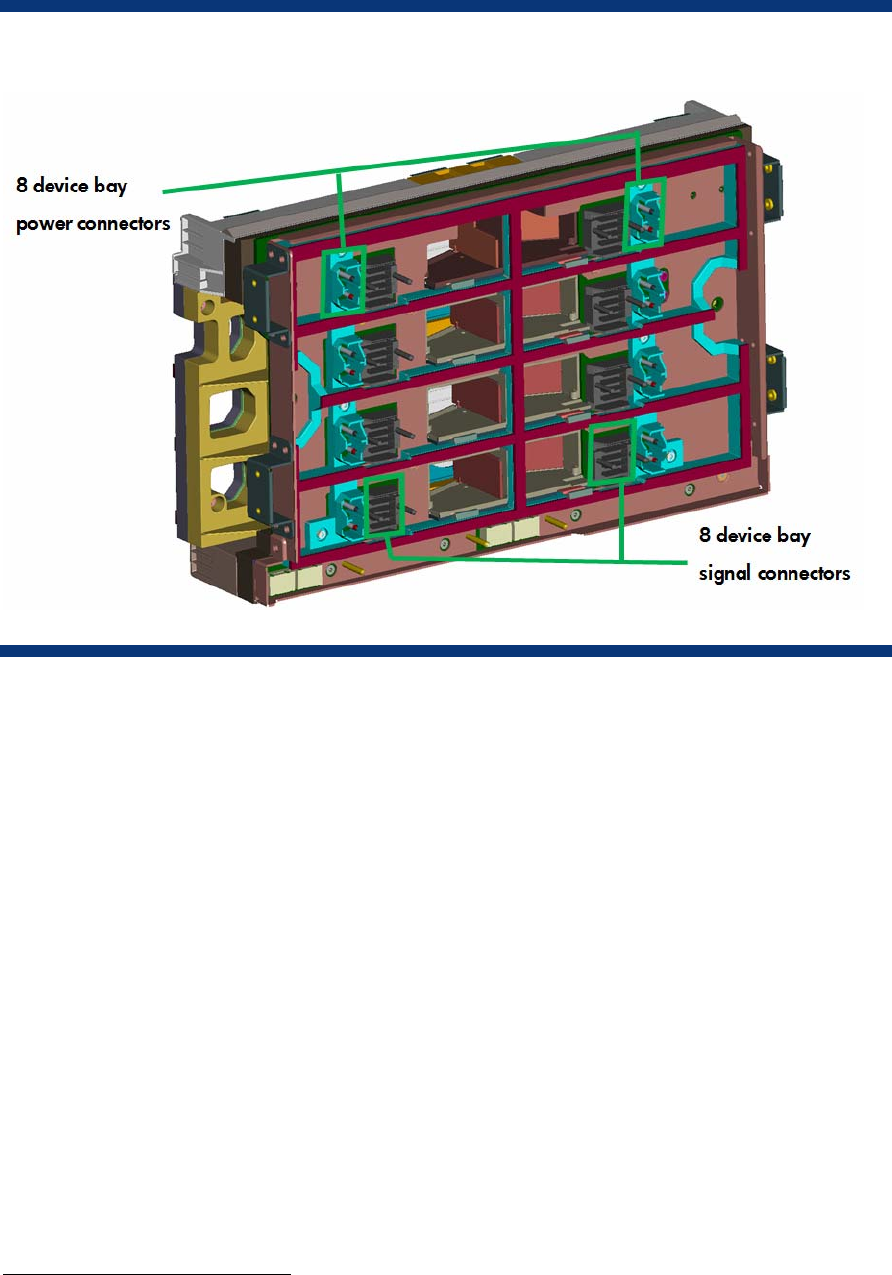
Figure 8. Diagram of the HP BladeSystem c3000 signal midplane
By taking advantage of the similar four-wire differential transmit and receive mechanism, the NonStop
signal midplane can support either network-semantic protocols (such as Ethernet, Fibre Channel, and
InfiniBand) or memory-semantic protocols (PCIe), using the same signal traces.
3
Figure 9 illustrates
how the physical lanes can be logically overlaid onto sets of four traces. Interfaces such as Gigabit
Ethernet (1000-base-KX) or Fibre Channel need only a 1x lane, or a single set of four traces. Higher
bandwidth interfaces, such as InfiniBand DDR, use up to four lanes.
3
Network-semantic interconnect protocols use network addresses in the packet headers to exchange data
between two nodes such as MAC addresses and IP addresses for Ethernet, world-wide port name for FC, or
GUID for InfiniBand. Memory-semantic interconnect protocols use memory addresses in the packet headers to
deposit or retrieve data where these addresses can be memory-mapped registers of a chip or system memory
location.
14


















