83-493-001 Rev. K
16
Peak Charge Rate = C - OUTPUT LOAD CAPACITOR
1
2
CV
2
T
C
V - PROGRAMMED OUTPUT VOLTAGE
Average Charge Rate = T
C
AND T
P
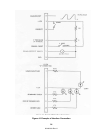
ARE SHOWN IN FIGURE
1
2
CV
2
T
p
VOLTAGE
TIME
Tc Tp
CHAPTER 5 APPLICATIONS
For clarification and further technical assistance specific to your applications, please
contact TDK-Lambda Americas Inc.
5.1 DETERMINING CAPACITOR CHARGE TIME
The ratings of these supplies are as follows: 500A – 500 J/s, 102A – 1000 J/s, 152A –
1500J/s, 202A-2000J/s average charge rate. Although the measure of Joules/sec
equates to Watts, Stored Energy per unit time is more convenient when working with
energy storage capacitors. The peak charge rate determines the capacitor charge time.
The average charge rate determines the total power delivered from the power supply. It
is possible to charge a capacitor at 1650 J/sec, but to discharge it at a low rep. rate
producing an average of 100 J/sec. The following formulas can be used to determine the
average and peak charge rate.
Figure 5-1 Output Voltage Waveform
5.2 VOLTAGE REVERSAL
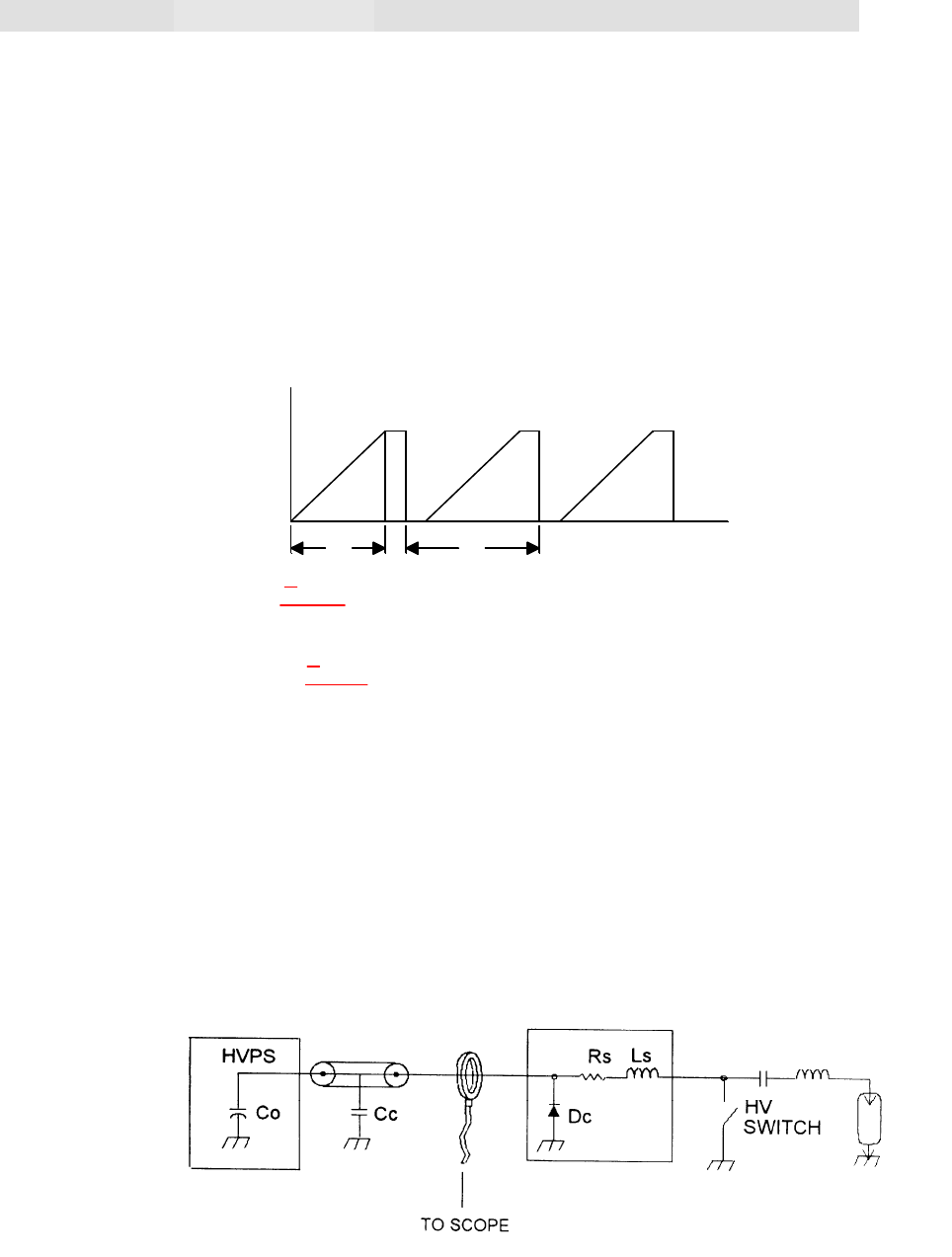
When the capacitor or PFN is discharged, a high peak current may flow out of the power
supply as a result of voltage reversal. This occurs in a system which is underdamped in
order to clear the high voltage switch after each pulse. The average value of this peak
current added to the normal output current may exceed the rating of the HV diodes in the
power supply. This current can be measured with a current transformer as shown in
Figure 5.2.
Figure 5-2 Output Current Measurement
T
C
and T
P
are shown in figure
Average Charge Rate =