18
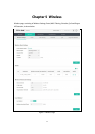
Encryption: Select the encryption type, including Auto, TKIP, and AES. The default setting is
Auto, which can select TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) or AES (Advanced
Encryption Standard)
automatically based on the wireless station's capability
and request. AES is more secure than TKIP and TKIP is not supported in 802.11n
mode. It is recommended to select AES as the encryption type.
Wireless
Password:
Configure the WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK password
with ASCII or Hexadecimal
characters. For ASCII, the length should be between 8 and 63 characters with
combination of numbers, letters (case-sensitive) and common punctuations. For
Hexadecimal, the length should be 64 characters (case-insensitive, 0-9, a-f, A-F).
Group Key
Update Period:
Specify the group key update period in seconds. The value can be either 0 or at
least 30. 0 means no update.
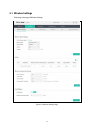
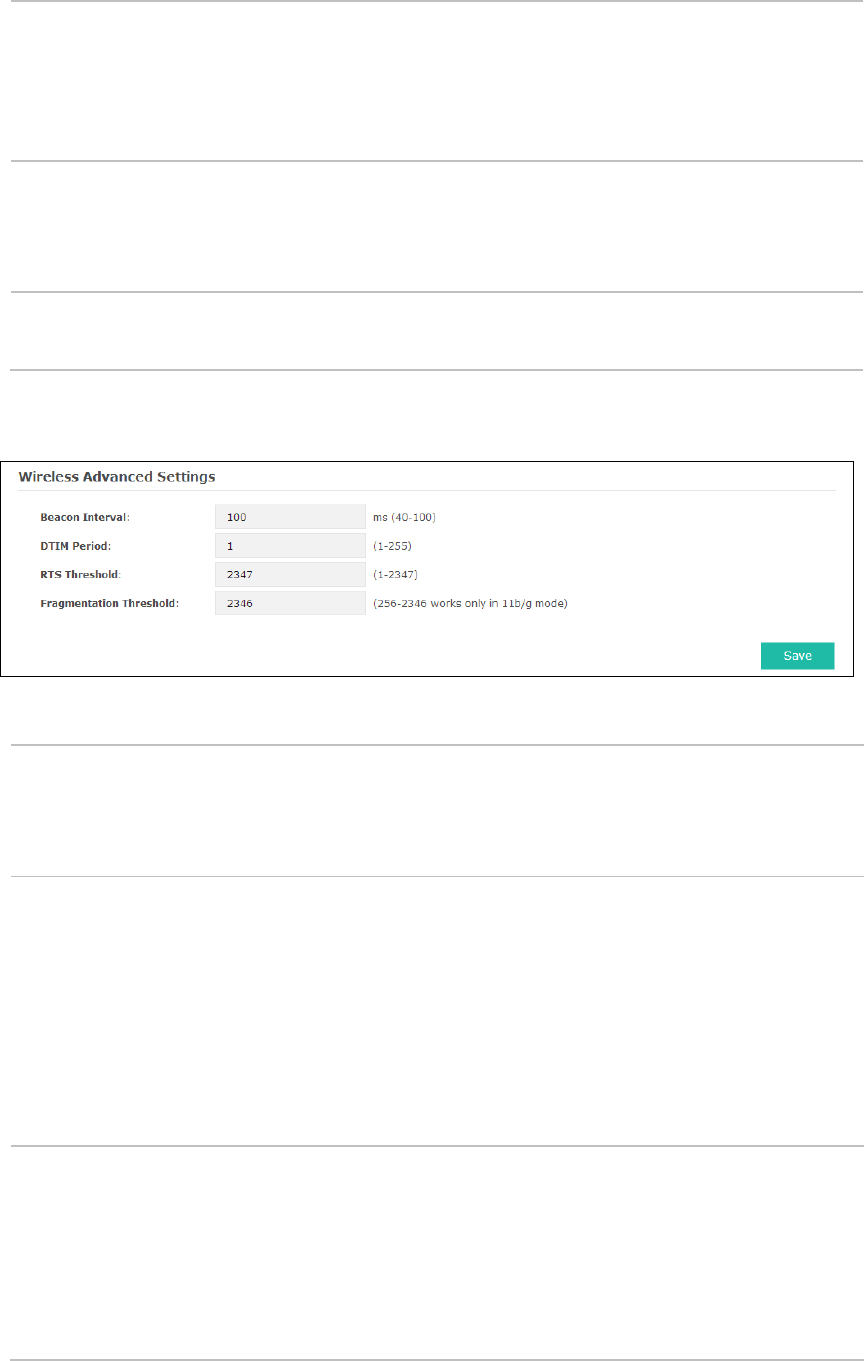
5.1.3 Wireless Advanced Settings
Figure 5-8 Wireless Advanced Settings
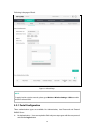
Beacon
Interval:
Beacons are transmitted periodically by the device to announce the presence of a
w
ireless network for the clients. Beacon Interval value determines the time
interval of the beacons sent by the device. You can specify a value from 40 to 100.
The default value is 100 milliseconds.
DTIM Period:
This value indicates the number of beacon intervals between successive Delivery
Traffic Indication Messages (DTIMs) and this number is included in each Beacon
frame. A DTIM is contained in Beacon frames to indicate whether the access point
has buffered broadcast and/or multicast data for the client devices. Following a
Beacon frame containing a DTIM
, the access point will release the buffered
broadcast and/or multicast data, if any exists. You can specify the value between
1-255 Beacon Intervals. The default value is 1, indicating the DTIM Period is the
same as Beacon Interval. An excessive DTIM period may reduce the performance
of multicast applications. It is recommended to keep it by default.
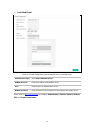
RTS Threshold:
When the RTS threshold is activated, all the stations and APs follow the Request
to Send (RTS) protocol. When the station is to send packets, it will send a RTS to
AP to inform the AP that it will send data. After receiving the RTS, the AP notices
other stations in the same wireless network to delay their transmitting of data. At
the same time, the AP inform the requesting station to send data. The value range
is from 1 to 2347 bytes. The default value is 2347, which means that RTS is
disabled.