TD-8816 ADSL2+ Modem Router User Guide
39
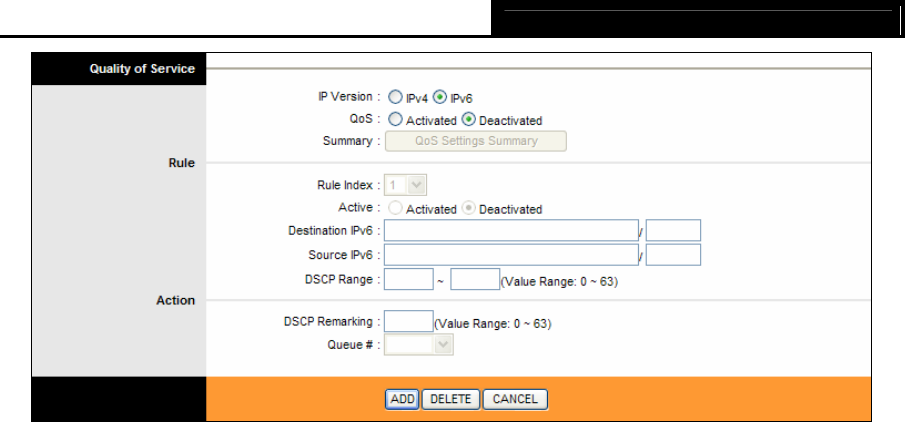
Figure 4-29
¾ QoS: Select this option to Activate/Deactivate the IP QoS on different types.
¾ Summary: Click the button to view the configurations of QoS.
¾ Rule: Configure the rules for QoS. If the traffic complies with the rule, then the modem router
will take the corresponding action to deal with it.
• Rule Index: Select the index for the rule you want to configure.
• Active: Activate the rule. The rule can take effect only when it is activated.
• Destination IPv6: Enter the IP information about the Destination host for the rule.
• Source IPv6: Enter the IP information about the Source host for the rule.
• DSCP Range: Enter the DSCP range to differentiate the traffic.
When you select DSCP, you can assign the priority via DHCP (the header of IP group). It maps
the IP group into corresponding service class.
¾ Action: Configure the action that the modem router takes to deal with the traffic which accord
with the rule.
• DSCP Remarking: Enter the number to remark the DSCP priority.
• Queue #: Select the priority type for the action.
4.4.5 VLAN
Choose “Advanced Setup→VLAN”, you can activate the VLAN function in the next screen.
Virtual LAN (VLAN) is a group of devices on one or more LANs that are configured so that they
can communicate as if they were attached to the same wire, when in fact they are located on a
number of different LAN segments. Because VLANs are based on logical instead of physical
connections, it is very flexible for user/host management, bandwidth allocation and resource
optimization. There are two types of VLAN as follows:
Port-Based VLAN: Each physical switch port is configured with an access list specifying
membership in a set of VLANs.
ATM VLAN: Using LAN Emulation (LANE) protocol to map Ethernet packets into ATM cells and
deliver them to their destination by converting an Ethernet MAC address into an ATM address.