5
MANAGING STORAGE ON THE WD SENTINEL SERVER
42
WD SENTINEL DS5100/DS6100
ADMINISTRATOR AND MAINTENANCE GUIDE
Managing Storage on the WD Sentinel Server
WD Sentinel Server RAID Storage
Storage Spaces
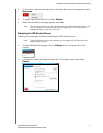
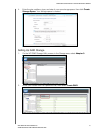
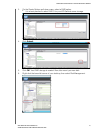
Setting Up Your Drives
Using USB Storage
Moving a Server Folder
WD Sentinel Server RAID Storage
RAID is the acronym for Redundant Array of Independent Disks. The WD Sentinel server
provides automatic RAID service to assure the integrity of the storage system. For
redundancy, a minimum of two drives must be active. The operating system and all data are
protected by the RAID structure. The server automates the management of the RAID.
Your WD Sentinel server uses RAID 5, which offers fast performance by striping data across
all drives, This RAID level provides the system with both redundancy and optimum capacity.
If a drive in the array fails, the data and operating system are still intact, and the
WD Sentinel server continues to provide service.
The WD Sentinel server lets you know when a drive fails in the following ways:
The LED below the bad drive is solid red.
The Power LED on the WD Sentinel server flashes red, indicating a serious fault.
An email Alert is posted if you have set it up to do so. (See “Monitoring System
Health and Alerts” on page 33.)
To recover from a failed drive, simply replace the drive (the one with the red LED over the
drive) with an approved drive for the WD Sentinel server (see “Find compatible hard drives”
on page 36)
Once replaced, complete the steps outlined in “Recovering from a Failed Drive” on page 48
to integrates the new drive into the RAID array. This process takes many hours to
accomplish. Progress of this operation appears on the Dashboard. While the server is
verifying the RAID array, your data continues to be available although the performance may
be impacted.
The WD Sentinel server RAID system has no downgrade options. Once available capacity
has been increased, the Administrator cannot decide to subsequently reduce capacity by
removing a drive. The removal of a drive degrades the RAID and makes it vulnerable to
single drive failure.
2 TB Drives 3 TB Drives 4 TB Drives
RAID Level 5 (4
Drives)
8 TB Capacity 12 TB
Capacity
16 TB
Capacity
Important: If you have one bad drive, the server operates normally. However, if a
second drive fails, the server will no longer operate. You will need to
recover the server and/or replace the failed drive(s). A best practice
is to have a replacement drive readily available.