Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
March 2001 Page 78
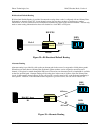
Bi-directional Default Routing
Bi-directional Default Routing is provided for automatic routing when a node is configured with two Primary Rate
D channels as shown in Figure 29. In two channel systems, the user does not have to configure any routing
information, as all calls received on one D channel are automatically routed to the second D channel. The user only
needs to enter routing information for those calls destined to a local HSU or FXS ports.
D ch 1
D ch 2
HSU/FXS
Default
IMACS
PBX
ISDN
Switch
Figure 29—Bi-Directional Default Routing
Alternate Routing
Alternate routing is provided for calls to take an alternate path in the event of a congested or failed primary trunk.
When there are more than two Primary Rate D channels, phone numbers can be assigned to more than one D
channel. Calls placed or routed through the PRI server will now have an alternate route if no bandwidth is available
on the first specified path. Alternate routing will also take place in the event of a failure of the first Primary Rate
circuit. In the example shown in Figure 30, the call from D1 is usually routed to D2, as the D channel numbering is
more specific. However, if the D2 trunk become congested or go out of service, the call will be routed to D3.
Dial 415 - 6xxx
415-6xxx
415-xxxx
D1
D2
D3
IMACS
PBX
ISDN
Switch
ISDN
Switch
Figure 30—Alternate Routing