Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
March 2001 Page 85
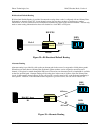
• Support data rates up to 128 kbps over single twisted
pair over 5Km
• DDS CSU / DSU replacement with BRI-NTU scenarios
.
64/128Kbps
Frame Relay
64/128Kbps
Frame Relay
T1/E1
Ethernet
BRI Cards provide 2B1Q IDSL termination
FRS provides IDSL concentration
NTU
IMACS
Frame Relay
Network
Ethernet
Router
2B1Q
Router
2B1Q
NTU
Router
2B1Q
NTU
Ethernet
64/128Kbps
Frame Relay
Figure 34—IDSL Service Provisioning
Grooming and Concentration in Cellular Networks
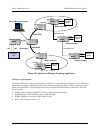
Figure 35 shows how a remote cell site uses an IMACS, trademarked “CellDAX” for all cellular environments, to
transport cellular voice and data traffic to the Mobile Switch Center (MSC). At the MSC, a DCS directs the CDPD
traffic (typically, a single DS0) from each of the 96 cell sites to the IMACS at same MCS. Because CDPD uses
HDLC framing the traffic from the 96 DS0s can be encapsulated by the two Frame Relay server cards located in the
IMACS. Each Frame Relay server can take in 64 DS0s directly into ports. Typically the CDPD traffic is bursty and
often less than one full DS0 and so can be groomed and concentrated by the Frame Relay server down to 48 or 24
DS0s depending upon the level of concentration needed. This results in a net savings of two or three T1/E1 spans
across the regional MSCs respectively. The MD-IS (Mobile Data Intermediate System) then processes the traffic
and routes it to the appropriate destinations.