61225101L1-5B 13
Bit Error Rate Test
The SHDSL NTU contains a built-in Bit Error Rate
Test (BERT). The BERT involves injecting and
detecting a Pseudorandom Binary Sequence (PRBS)
toward the network on the selected payload (i.e.
G.703, Nx64, or entire SHDSL payload). The PRBS
used in the SHDSL NTU is PRS15 as defined in
ITU-T O.150 and O.151. It is also known as a 2e-15
pattern.
The BERT is only accessible via the VT100 terminal
screens. Select “4. Test” from the Main Menu
Screen. From the Test Screen, the SHDSL BERT,
G.703 BERT, and Nx64k BERT options will appear,
and each has one of the following status messages:
N/A – This BERT is currently unavailable. Only one
BERT can be active at a time. For example, if
SHDSL BERT is active, all others will be N/A.
ACTIVE – This BERT is currently in progress. The
source column identifies the person who initiated the
BERT.
INACTIVE – This BERT is not currently in progress.
After selecting a BERT type from the Test Screen, the
BERT Screen will appear, illustrating both BERT
statistics and commands.
If no BERT is currently active, the following list of
commands will be available:
Start – Starts the BERT on the selected port/service.
If the BERT is currently active, the following list of
commands will be available:
Stop – Stops the BERT in progress.
Inject a Single Bit Error – Injects one bit error into
the pattern.
Restart – Clears out all statistics and restarts the
BERT.
In addition to the commands, the following statistical
information is provided:
Bit Error Rate – Total number of bit errors divided
by the total number of bits in the current test interval.
Bit Error Count – Total number of bit errors in the
current test interval.
Pattern Sync Loss Count – Total number of times
that the BERT has lost pattern sync.
Errored Seconds – Total number of seconds in which
at least one bit error has occurred.
Total Elapsed Time – Total time that has elapsed
since the test began (Days: Hours: Minutes: Seconds).
A BERT status field supplies the following
information:
On – The BERT has started and has pattern sync.
Searching for pattern – The BERT has lost pattern
sync.
Off – This BERT is currently off.
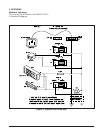
Loopbacks
There are five types of local loopbacks and five types
of remote loopbacks available for each of the three
line interfaces (V.35, G.703, and SHDSL). When
initiating a loopback, the first step is choosing a line
interface. When V.35 is chosen, the loopback will
occur at the V.35 drivers and receivers. When G.703
is chosen, the loopback will occur at the G.703 drivers
and receivers. When SHDSL is chosen, the loopback
will occur at the SHDSL drivers and receivers.
NOTE
All remote loopbacks are initiated at the local
Express 6530 unit.
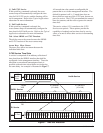
Local Dual Sided Loopback – Provides a
bidirectional loopback at the NTU (Figure 12).
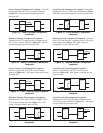
Remote Dual Sided Loopback – Initiated at the NTU
and provides bidirectional loopback at the LTU
(Figure 13).
Figure 13. Remote Dual Sided Loopback
Figure 12. Local Dual Sided Loopback