Host RJ-11 IP Gateway User Guide, version 25
Configuration Settings and Commands
imposes limits on source TCP ports then you may need to set this to something specific. Note that
if you specify something other than 0, you will be limited to only 1 TCP pipe at-a-time for any
given destination port.
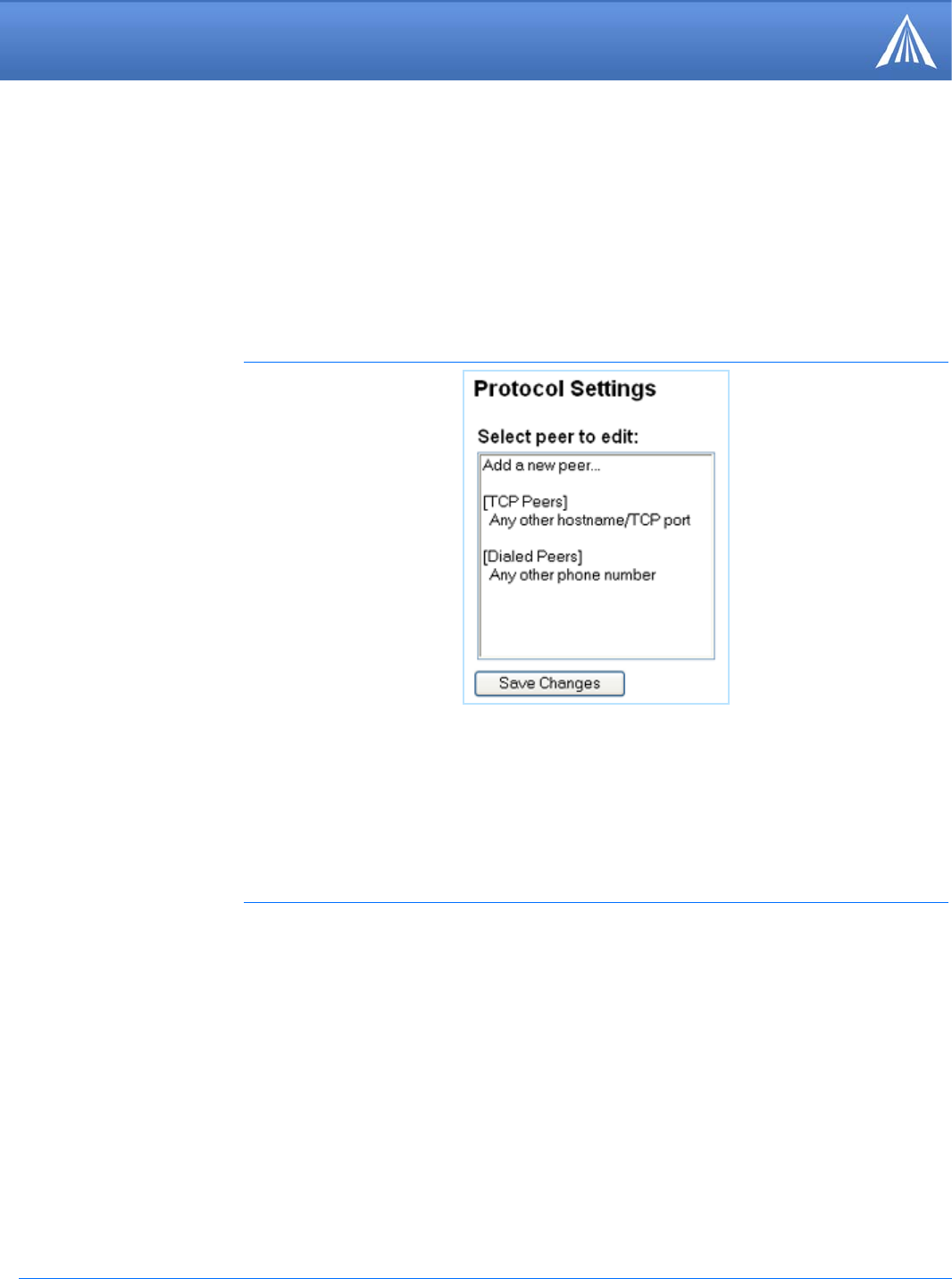
Protocol Settings
For each host (peer) you will make an outgoing connection to, you need to specify the protocol
options used for that host. For each host, select the Host from the “Edit settings for a different peer”
selection box. Select “Add a new peer definition” link to add a new host.
FIGURE 8. Host RJ-11 IP Gateway: Protocol Settings
The hosts are identified by their IP address or Hostname and TCP port. You may also specify wild
cards. Specific host names and/or port numbers take precedence over the wild cards. An asterisk
for the IP address/hostname (for instance “*:443”) means any other host when connecting on port
443. An asterisk for the port number (for instance “host.peer.com:*”) refers to any other port on
that host. And a double asterisk (“*:*”) refers to all other hosts.
Network Configuration
The Network Configuration group configures settings for the RJ-45 Ethernet port.
Network Settings
The Network Settings page allows you to set the IP address, the IP netmask, and the TCP keep-
alive settings.
Every IP address contains two pieces of information: the network number and the host number. A
network number is assigned to each local area network and is shared by all the network devices on
that network. Each network device, or “host”, is assigned a unique host number. The IP netmask
defines which portion of an IP address contains the network number, and which portion contains
the host number. The default netmask depends on the “class” of the IP address that you are using.