Chapter 7 Electrical Data 35
31994A —1 August 2004 AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet
7.12 Thermal Diode Characteristics
The AMD Sempron processor model 10 provides a diode that
can be used in conjunction with an external temperature sensor
to determine the die temperature of the processor. The diode
anode (THERMDA) and cathode (THERMDC) are available as
pins on the processor, as described in
“THERMDA and
THERMDC Pins” on page 73.
For information about thermal design for the AMD Sempron
processor model 10, including layout and airflow
considerations, see the AMD Processor Thermal, Mechanical, and
Chassis Cooling Design Guide, order# 23794, and the cooling
guidelines on http://www.amd.com.
Thermal Diode
Electrical
Characteristics
Table 13 shows the AMD Sempron processor model 10
characteristics of the on-die thermal diode. For information
about calculations for the ideal diode equation and
temperature offset correction, see Appendix A, "Thermal
Diode Calculations," on page 77.
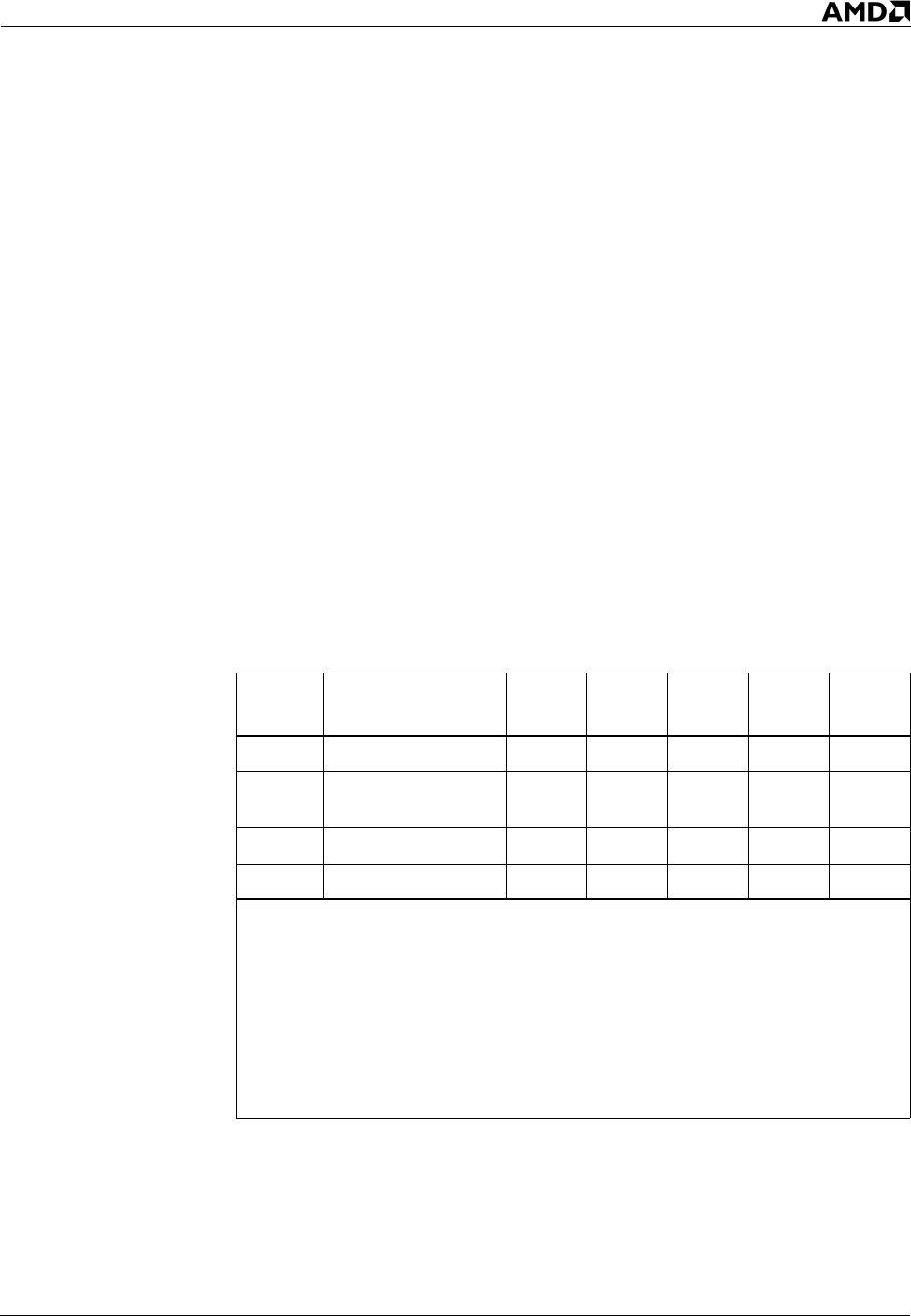
Table 13. Thermal Diode Electrical Characteristics
Symbol
Parameter
Description
Min Nom Max Units Notes
I
Sourcing current 5300µA1
n
f, lumped
Lumped ideality
factor
1.00000 1.00374 1.00900 2, 3, 4
n
f, actual
Actual ideality factor 1.00261 3, 4
R
T
Series Resistance 0.93 Ω 3, 4
Notes:
1. The sourcing current should always be used in forward bias only.
2. Characterized at 95°C with a forward bias current pair of 10 µA and 100 µA. AMD
recommends using a minimum of two sourcing currents to accurately measure the
temperature of the thermal diode.
3. Not 100% tested. Specified by design and limited characterization.
4. The lumped ideality factor adds the effect of the series resistance term to the actual ideality
factor. The series resistance term indicates the resistance from the pins of the processor to the
on-die thermal diode. The value of the lumped ideality factor depends on the sourcing current
pair used.