Chapter 6 Advanced 333 Front-Side Bus AMD Athlon™ XP Processor Model 10 Specifications 21
26237C—May 2003 AMD Athlon™ XP Processor Model 10 Data Sheet
Preliminary Information
6 Advanced 333 Front-Side Bus AMD Athlon™ XP
Processor Model 10 Specifications
This chapter describes the electrical specifications that are
unique to the advanced 333 front-side bus (FSB)
AMD Athlon™ XP processor model 10.
6.1 Electrical and Thermal Specifications for the Advanced 333 FSB
AMD Athlon™ XP Processor Model 10
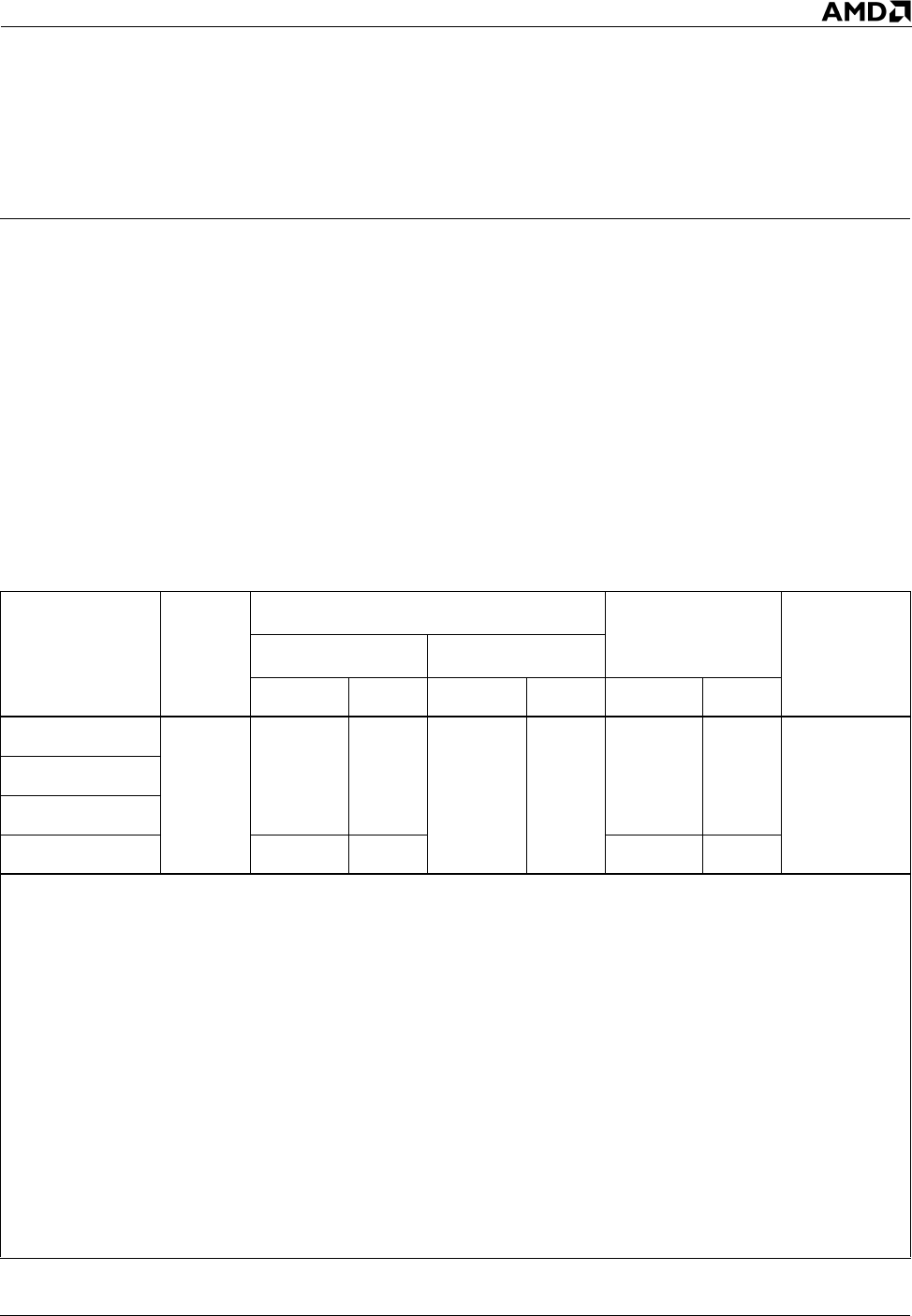
Table 1 shows the electrical and thermal specifications in the
C0 working state and the S1 Stop Grant state for this processor.
Table 1. Electrical and Thermal Specifications for the Advanced 333 FSB AMD Athlon™ XP Processor
Model 10
Frequency in MHz
(Model Number)
V
CC_CORE
(Core
Voltage)
I
CC
(Processor Current)
Thermal Power
5
Maximum Die
Temperature
Working State C0
Stop Grant S1
1, 2, 3, 4
Maximum Typical Maximum Typical Maximum Typical
1833 (2500+)
1.65 V
41.4 A 32.5 A
12.1 A 7.2 A
68.3 W 53.7 W
85°C
1917 (2600+)
2083 (2800+)
2167 (3000+)
45.0 A 35.4 A 74.3 W 58.4 W
Notes:
1. See Figure 3, "AMD Athlon™ XP Processor Model 10 Power Management States" on page 9.
2. The maximum Stop Grant currents are absolute worst case currents for parts that may yield from the worst case corner of the
process and are not representative of the typical Stop Grant current that is currently about one-third of the maximum specified
current.
3. These currents occur when the AMD Athlon™ system bus is disconnected and has a low power ratio of 1/8 for Stop Grant
disconnect and a low power ratio of 1/8 Halt disconnect applied to the core clock grid of the processor as dictated by a value of
2003_1223h programmed into the Clock Control (CLK_Ctl) MSR. For more information, refer to the AMD Athlon™ and
AMD Duron™ Processors BIOS, Software, and Debug Developers Guide, order# 21656.
4. The Stop Grant current consumption is characterized at 50°C and not tested.
5. Thermal design power represents the maximum sustained power dissipated while executing publicly-available software or
instruction sequences under normal system operation at nominal V
CC_CORE
. Thermal solutions must monitor the temperature of
the processor to prevent the processor from exceeding its maximum die temperature.


















