Chapter 11 Avaya P330 Layer 2 Features
110 Avaya P334T-ML User’s Guide
Port Mirroring Configuration
Port Mirroring Overview
Port Mirroring copies all received and transmitted packets (including local traffic)
from a source port to a predefined destination port, in addition to the normal
destination port of the packets. Port Mirroring, also known as “sniffing” is useful in
debugging network problems.
Port mirroring allows you to define a source port and a destination port, regardless
of port type. For example, a 10 Mbps and a 100 Mbps port can form a valid source/
destination pair. You cannot, however define the port mirroring source and
destination ports as the same port.
You can define one source port and one destination port on each C460 chassis for
either received – Rx – or transmitted and received – Tx + Rx – traffic.
Port Mirroring CLI commands
Port Mirroring Constraints
Note the following limitations:
• The VLAN binding parameters of the source and destination ports must be
identical.
• Ports which are members in a Link Aggregation Group (LAG) cannot also be
used as Port Mirroring Destination or Source ports.
• Within the P334T-ML switch, port mirroring can be configured between ports in
the three following groups:
— 1-12, 25-36
— 13-24, 37-48
—51, 52
• On the stack level, port mirroring pairs can be configured between any Giga
port, and between any Giga port on the P334T-ML and any 10/100Mbps port
not residing on a P334T-ML.
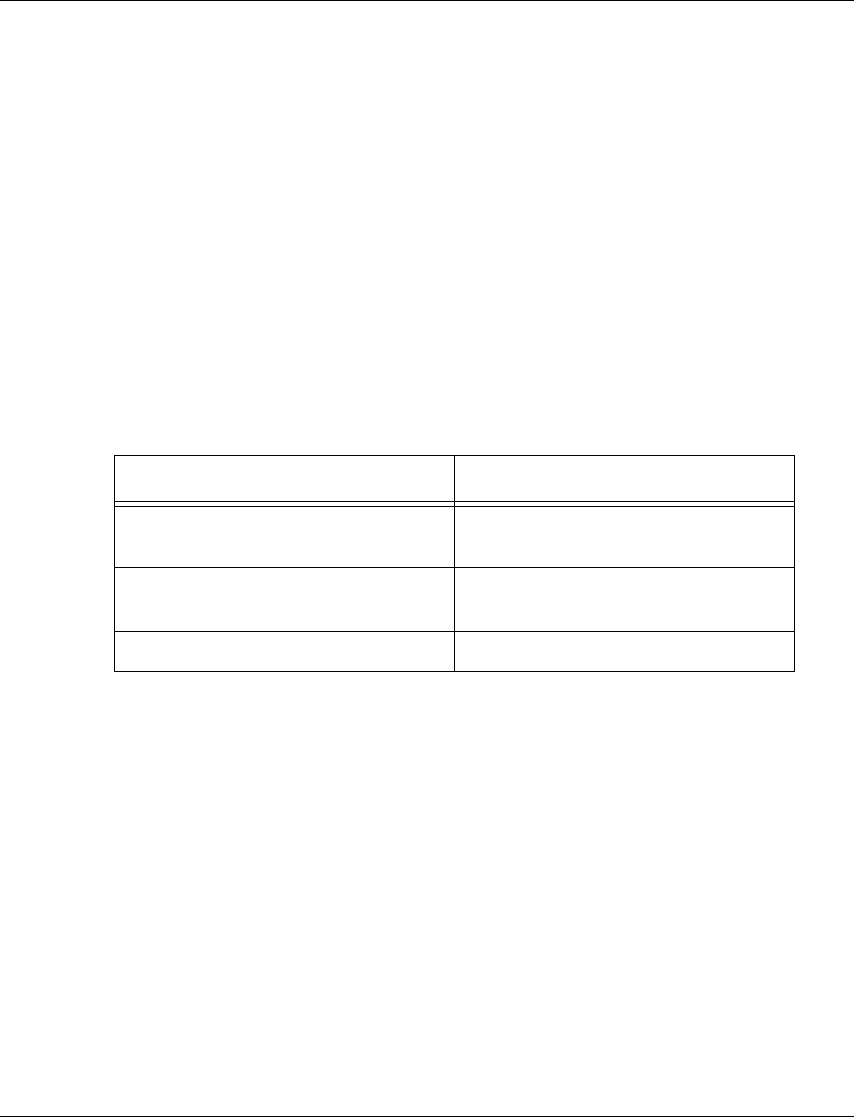
In order to... Use the following command...
Define a port mirroring source-
destination pair in the switch
set port mirror
Display port mirroring information
for the switch
show port mirror
Cancel port mirroring clear port mirror