31
IP addresses appear in dotted decimal (rather than in binary)
notation. Dotted decimal notation divides the 32-bit value into
four 8-bit groups, or octets, and separates each octet with a
period. For example, 199.217.132.1 is an IP address in dotted
decimal notation.
To accommodate networks of different sizes, the IP address
has three divisions—Classes A for large, B for medium, and C
for small. The difference among the network classes is the
number of octets reserved for the network ID and the number
of octets reserved for the host ID.
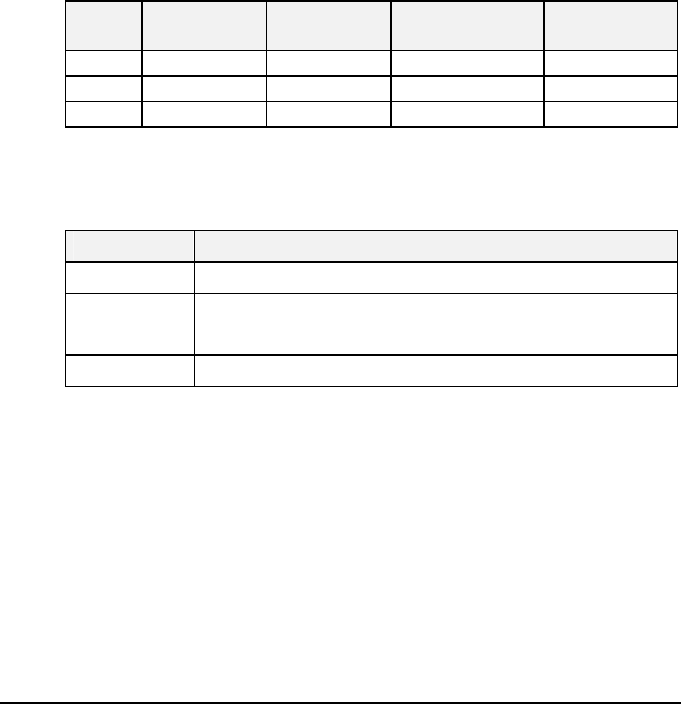
Class Value of First
Octet
Network ID Host ID Number of Hosts
A 1-126 first octet last three octets 16,387,064
B 128-191 first two octets last two octets 64,516
C 192-223 first three octets
last octet 254
Any value between 0 and 255 is valid as a host ID octet except
for those values the InterNIC reserves for other purposes.
Value Purpose
0, 255 Subnet masking
127
Loopback testing and interprocess communi-
cation on local devices
224-254 IGMP multicast and other special protocols
Subnetting and Subnet Masks
Subnetting divides a network address into subnetwork
addresses to accommodate more than one physical network on
a logical network.
For example: A Class B company has 100 LANs (Local Area
Networks) with 100 to 200 nodes on each LAN. To classify
the nodes by its LANs on one main network, this company