E-43
Examples of Calculation Results Using Polar
Coordinate Format (
r ∠
θ
)
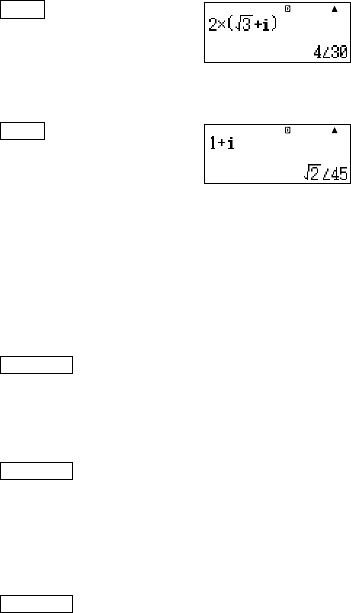
Example 1: 2 × ('3 + i) = 2'3 + 2i = 4 ∠ 30 (Angle Unit: Deg)
MATH
2*(!3e+i)=
Math
CMPLX
•With Linear format, the absolute value and argument are shown in
two different lines.
Example 2: 1 + i = '2 ∠ 45 (Angle Unit: Deg)
MATH
1+i=
Math
CMPLX
•Argument
θ
is output in the range of –180°<
θ
< 180°.
Specifying the Calculation Result Display Format
You can override complex number display settings and specify the
format that should be used to display calculation results.
•To specify rectangular coordinate format for the calculation result,
perform the following key operation at the end of the calculation.
12(CMPLX)4('a+bi
)
•To specify polar coordinate format for the calculation result, perform
the following key operation at the end of the calculation.
12(CMPLX)3('r∠
θ
)
Appendix <#049> 1 + i (= '2 ∠ 45) = 1.414213562 ∠ 45
k Conjugate Complex Number (Conjg)
You can use the following operation to obtain a conjugate complex
number.
12(CMPLX)2(Conjg)
Appendix
<#050> Determine the conjugate of the complex number 2 + 3i.
k Absolute Value and Argument (Abs, arg)
You can use the following procedure to obtain the absolute value
(|Z|) and argument (arg) on the Gaussian plane for a complex number
of the format Z = a + bi.
1w(Abs); 12(CMPLX)1(arg)
Appendix
<#051> Obtain the absolute value and argument of 2 + 2i.
*1 Absolute Value *2 Argument


















