1-4
Cisco MWR 1900 Mobile Wireless Edge Router Software Configuration Guide
78-13983-04
Chapter1 Overview of the MWR 1900
Software Features
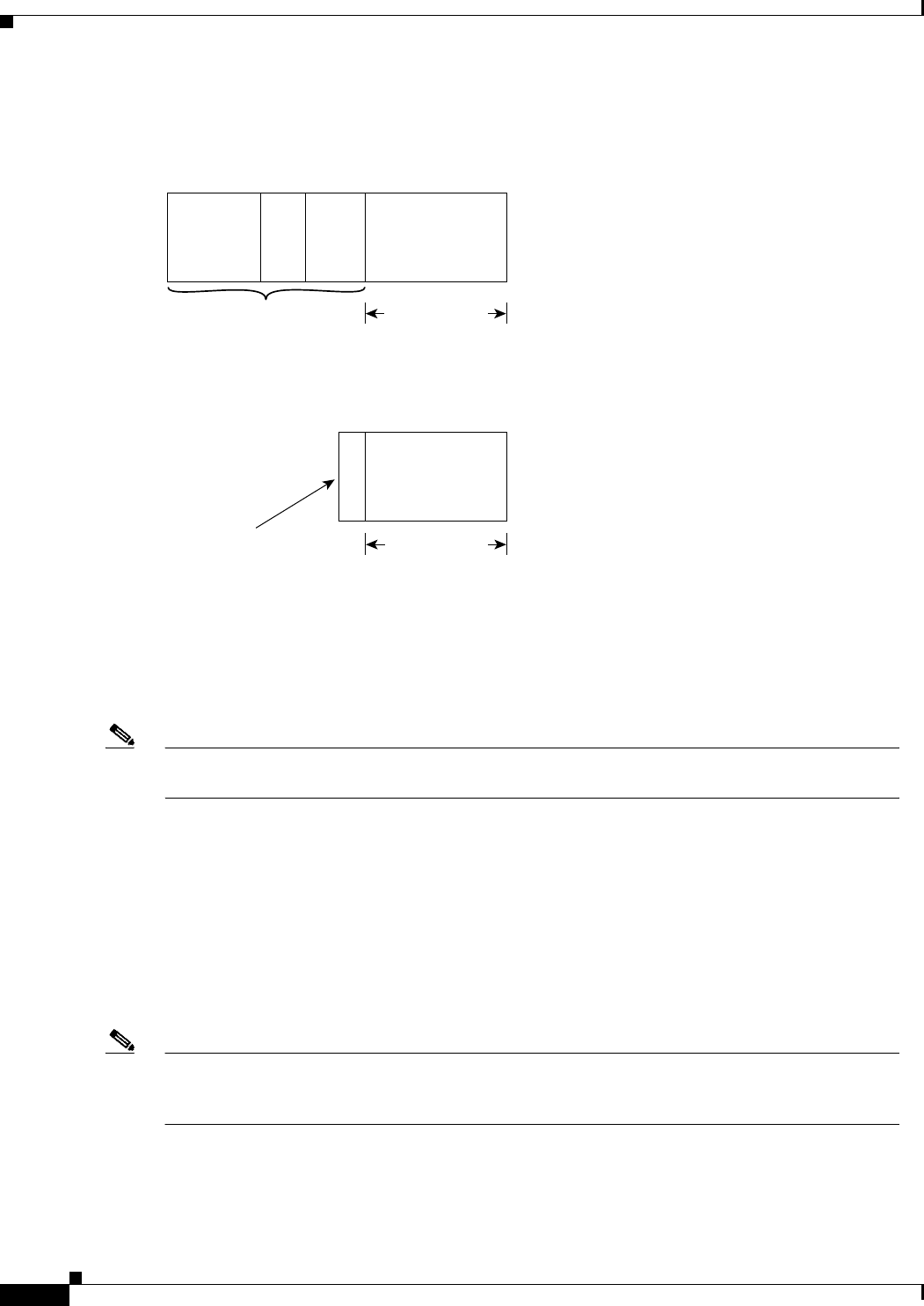
Figure 1-2 RTP Header Compression
RFCs 2508 and 2509 describe a method for compressing not only the RTP header, but also the associated
UDP and IP headers. Using this method, the 40 bytes of header information is compressed into
approximately 2 to 4 bytes, as shown in Figure 1-2. Because the frames are compressed on a link-by-link
basis, the delay and loss rate are lower, resulting in improved performance.
The MWR 1900 network processor offloads both the compression and decompression of RTP frames
from the Cisco IOS software.
Note The MWR 1900 router can be configured to perform only IP/UDP compression, in which case the
header is reduced from 28 bytes to 2 to 4 bytes.
Redundancy Support
To ensure availability, the backhaul links to an MWR 1900 router are redundantly cabled to the
VWIC-2MFT-T1-DIR/ VWIC-2MFT-E1-DIR cards. This card, designed specifically for the MWR 1900
router, is a modified 2-port T1/E1 Multiflex VWIC with Drop and Insert.The modifications include the
addition of relays to activate the T1/E1 ports. The relays allow “Y” cabling for router redundancy where
the T1/E1 link is not redundant and default to open. The relays are controlled by HSRP/redundancy
protocol between the two routers connected to the same T1/E1.
Note If you choose to use the MWR 1900 router in a non-redundant configuration, you must close the
relays on the card using the standalone subcommand. Also, redundancy parameters are processed
when the router is booted up. These parameters cannot be changed “on the fly.”
Before RTP header compression:
20 bytes 8 bytes
20 to 160 bytes
12 bytes
IP
Header
UDP
RTP Payload
After RTP header compression:
2 to 4 bytes
20 to 160 bytes
IP/UDP/RTP header
Payload
12076


















