4 ATM Cable Interface Processor (ACIP) Installation and Configuration
ACIP Description
An ATM connection transfers raw bits of information to a destination router/host. The ATM router
takes the common part convergence sublayer (CPCS) frame, carves it up into 53-byte cells, and
sends these cells to the destination router or host for reassembly. Forty-eight bytes of each cell are
used for the CPCS data; the remaining 5 bytes are used for cell routing. The 5-byte cell header
contains the destination VPI/VCI, payload type, cell loss priority (CLP), and header error control.
Unlike a LAN, which is connectionless, ATM requires certain features to provide a LAN
environment to the users. One such feature is broadcast capability. Protocols wanting to broadcast
packets to all stations in a subnet must be allowed to do so with a single call to Layer 2. In order to
support broadcasting, the router allows the user to specify a particular VC as a broadcast VC. When
the protocol passes a packet with a broadcast address to the ATM driver, the packet is duplicated and
sent to each VC marked as a broadcast VC. This method is known as pseudobroadcasting.
ACIP Description
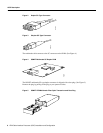
The ATM Cable Interface Processor (ACIP) (see Figure 1) provides a single ATM network interface
for a Cisco 7500 series router by providing a direct connection between the router’s high-speed
Cisco Extended Bus (CyBus) and external equipment. The ACIP can be connected directly to a
TeraLink 1000 cable headend, or through a Cisco Lightstream 1010 ATM switch or other external
ATM network equipment. The physical layer interface module (PLIM) on the ACIP provides a
SONET/SDH (STS-3C) interface connection.
Figure 1 ACIP with the UNI 155-Mbps Interface
ACIP Features
The ACIP supports the following features:
• Multiple rate queues.
• Reassembly of up to 512 buffers simultaneously. Each buffer represents a packet.
• Up to 2,048 virtual circuits.
• Transfer rates per VPI limited to fixed values provided by the cable headend.
• Exception queue, which is used for event reporting. Events such as CRC errors are reported to
the exception queue.
• Raw queue, which is used for all raw traffic over the ATM network. Raw traffic includes
Operation Administration and Maintenance (OAM) cells and Interim Local Management
Interface (ILMI) cells. (ATM signaling cells are not considered raw.)
H2337
UNI 155
U111, microcode ROM
TX RX
ENABLED
RX Carrier
RX Cells