2
Third-Generation Alpha Chip
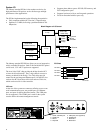
The third generation of the Alpha microprocessor, the Alpha
21264, is a superscalar, superpipelined implementation of the
Alpha architecture. The first offering of this chip, which was
manufactured using the CMOS-6 process, was known as EV6
and now the EV67 (21264A) chip is available, which uses the
CMOS-7 process. Over 15.2 million transistors are on one die.
In our discussion here, the Alpha 21264 designation applies to the
EV6 and the EV67 chips, unless we need to distinguish between
the two. Designed for performance, the Alpha 21264 achieves this
goal by carefully studied and simulated architectural and circuit
analysis. The 21264 memory system also enables the high per-
formance levels. On-chip and off-chip caches provide for very low
latency data access, which allows for very high bandwidth data
access. The 21264A 2-Mbyte off-chip cache runs at 205 MHz.
Internal to each chip is a 64-Kbyte instruction cache (I-cache)
and a 64-Kbyte data cache (D-cache).
• I-cache. 64 Kbytes, two-way set-associative, virtually
addressed cache with 64-byte blocks
• D-cache. 64 Kbytes, two-way set-associative, virtually
indexed, physically tagged, writeback cache with 64-byte
blocks
Chip Operation
Several key design choices were made in the chip architecture
to maximize performance: Four instructions are fetched each
cycle, and then how those instructions are handled boosts the
speed of execution. Register renaming assigns a unique storage
location with each write reference to a register, avoiding register
dependencies that can be a potential bottleneck to processor
performance.
Another design feature, out-of-order execution, permits
instructions to execute in an order different from the order that
the instructions are fetched. In effect, instructions execute as
soon as possible. This allows for faster execution since critical
path computations are started and completed as soon as
possible.
In addition, the Alpha 21264 employs speculative execution to
maximize performance. It speculatively fetches and executes
instructions even though it may not know immediately whether
the instruction will be on the final execution path. This is
particularly useful, for instance, when the 21264 predicts
branch directions and speculatively executes down the
predicted path. The sophisticated branch prediction in the
21264 coupled with the speculative and dynamic execution
extracts the most instruction parallelism from applications.
For more information about the chip, see
http://www.compaq.com/alphaserver/download/ev6chip.pdf
Alpha 21264 Features
• Out-of-order instruction execution
• Large (64 Kbyte) on-chip data and instruction caches
• Improved branch prediction through intuitive execution
• Register renaming
• Increased bandwidth for high-speed access to second-level
cache and system memory
• Motion video instructions
• Square root and divide instructions
• All instructions are 32 bits long and have a regular
instruction format
• Floating-point unit, supports DIGITAL and IEEE floating-
point data types
• 80 integer registers, 64 bits wide
• 72 floating-point registers, 64 bits wide