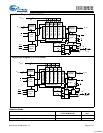
CY7C1307BV25
CY7C1305BV25
Document #: 38-05630 Rev. *A Page 6 of 21
When deselected, the write port will ignore all inputs after the
pending Write operations have been completed.
Byte Write Operations
Byte Write operations are supported by the CY7C1305BV25.
A write operation is initiated as described in the Write
Operation section above. The bytes that are written are deter-
mined by BWS
0
and BWS
1
, which are sampled with each set
of 18-bit data word. Asserting the appropriate Byte Write
Select input during the data portion of a write will allow the data
being presented to be latched and written into the device.
Deasserting the Byte Write Select input during the data portion
of a write will allow the data stored in the device for that byte
to remain unaltered. This feature can be used to simplify
Read/Modify/Write operations to a Byte Write operation.
Single Clock Mode
The CY7C1305BV25 can be used with a single clock that
controls both the input and output registers. In this mode the
device will recognize only a single pair of input clocks (K and
K
) that control both the input and output registers. This
operation is identical to the operation if the device had zero
skew between the K/K and C/C clocks. All timing parameters
remain the same in this mode. To use this mode of operation,
the user must tie C and C
HIGH at power-on. This function is
a strap option and not alterable during device operation.
Concurrent Transactions
The Read and Write ports on the CY7C1305BV25 operate
completely independently of one another. Since each port
latches the address inputs on different clock edges, the user
can Read or Write to any location, regardless of the trans-
action on the other port. If the ports access the same location
at the same time, the SRAM will deliver the most recent infor-
mation associated with the specified address location. This
includes forwarding data from a Write cycle that was initiated
on the previous K clock rise.
Read and Write accesses must be scheduled such that one
transaction is initiated on any clock cycle. If both ports are
selected on the same K clock rise, the arbitration depends on
the previous state of the SRAM. If both ports were deselected,
the Read port will take priority. If a Read was initiated on the
previous cycle, the Write port will assume priority (since Read
operations can not be initiated on consecutive cycles). If a
Write was initiated on the previous cycle, the Read port will
assume priority (since Write operations can not be initiated on
consecutive cycles). Therefore, asserting both port selects
active from a deselected state will result in alternating
Read/Write operations being initiated, with the first access
being a Read.
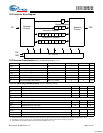
Depth Expansion
The CY7C1305BV25 has a Port Select input for each port.
This allows for easy depth expansion. Both Port Selects are
sampled on the rising edge of the positive input clock only (K).
Each port select input can deselect the specified port.
Deselecting a port will not affect the other port. All pending
transactions (Read and Write) will be completed prior to the
device being deselected.
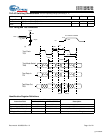
Programmable Impedance
An external resistor, RQ, must be connected between the ZQ
pin on the SRAM and V
SS
to allow the SRAM to adjust its
output driver impedance. The value of RQ must be 5X the
value of the intended line impedance driven by the SRAM, The
allowable range of RQ to guarantee impedance matching with
a tolerance of ±15% is between 175Ω and 350Ω
, with
V
DDQ
=1.5V. The output impedance is adjusted every 1024
cycles upon power-up to account for drifts in supply voltage
and temperature.
Note:
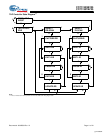
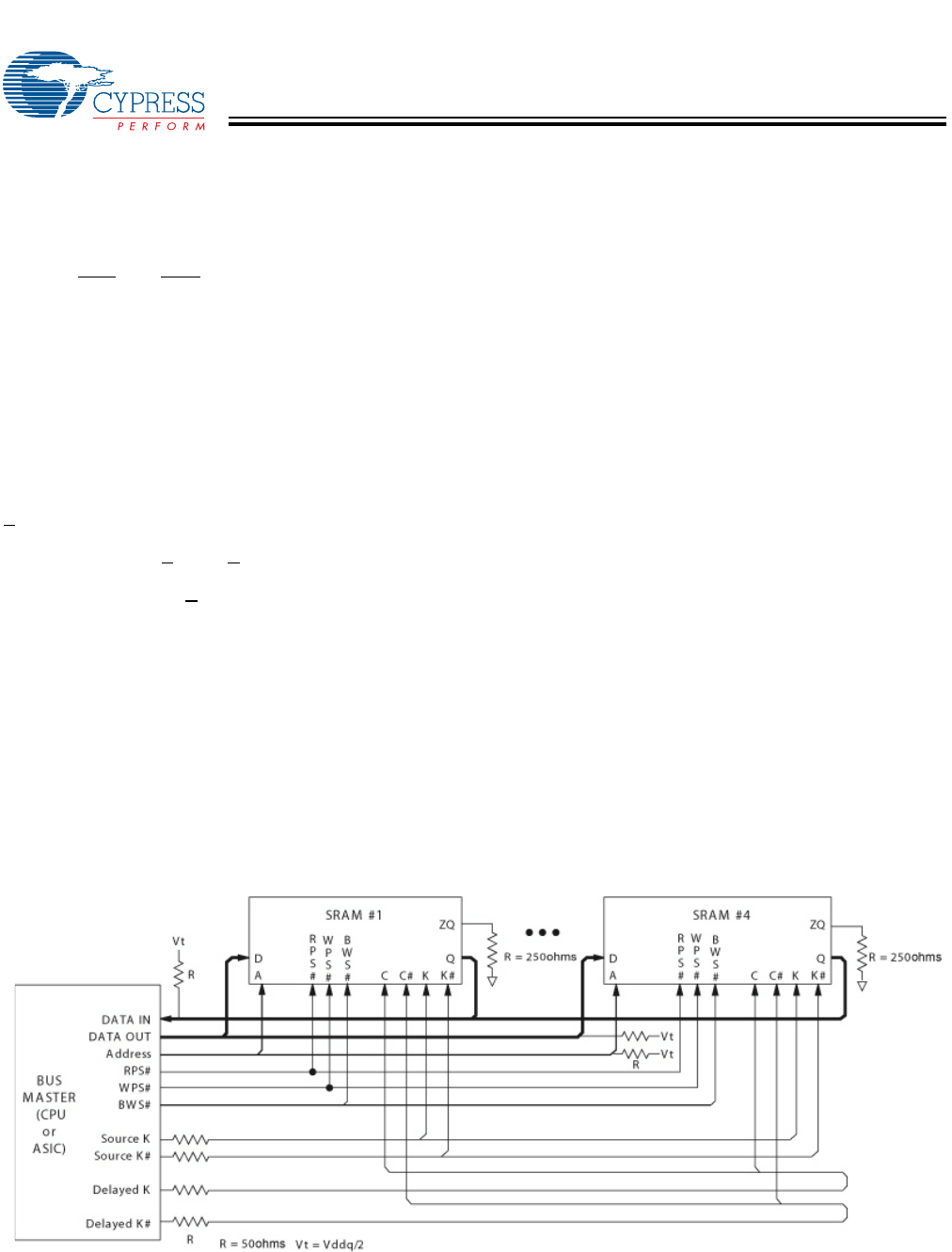
1. The above application shows four QDR-I being used.
Application Example
[1]
[+] Feedback