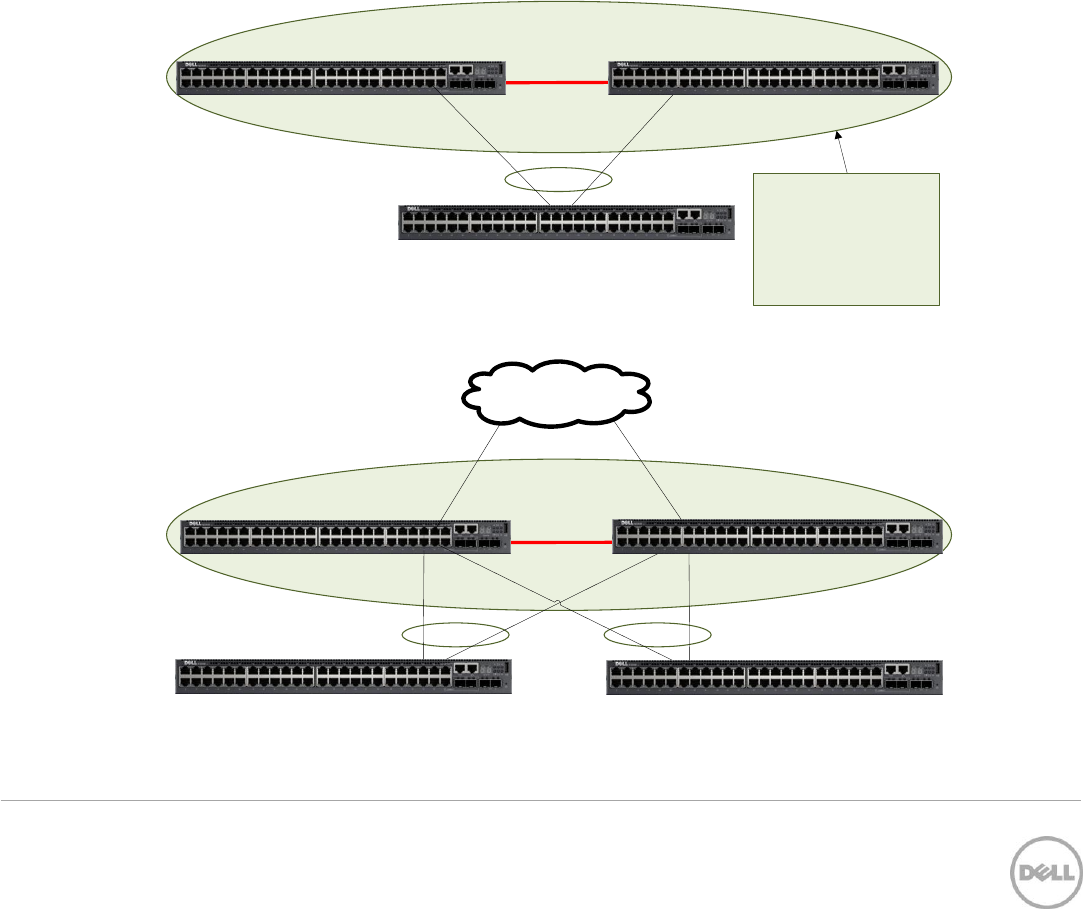
5 Using MLAG in Dell Networks
.
1 Introduction
MLAGs provide an active-active split aggregation deployment across two switches acting as one. MLAG
creates a more resilient network with higher bandwidth capabilities. This white paper discusses MLAGs,
how and when they are used, caveats to look out for, and instructions on how to implement MLAG into
your network.
Figure 1 below shows two very basic examples of MLAG domains. In both examples, peer switches are
linked together with a special LAG (one or more cables as denoted by the red line in the pictures below),
called a Peer-Link. With the Peer-Link configured, the two switches appear as a single switch to partner
switches upstream and downstream. Each partner switch contains MLAGs that are simply LAGs (ling
aggregation groups) whose cables are split between the two peers. Primary and secondary peer roles are
chosen automatically by the program when MLAG is enabled.
MLAG
Secondary MLAG peer
Peer-Link
MLAG
Secondary MLAG peer
Peer-Link
MLAG
Primary MLAG peer
Primary MLAG peer
Partner Switch
Partner Switch Partner Switch
MLAG peers appear
as a single logical
switch to partner
switches on the
network
Simple L2 MLAG
L3 MLAG with mulitple
partner switches
Two examples of a single-tier MLAG topology Figure 1


















