Modbus TCP Remote I/O Communication Module RTU-EN01
DVP-PLC Operation Manual
20
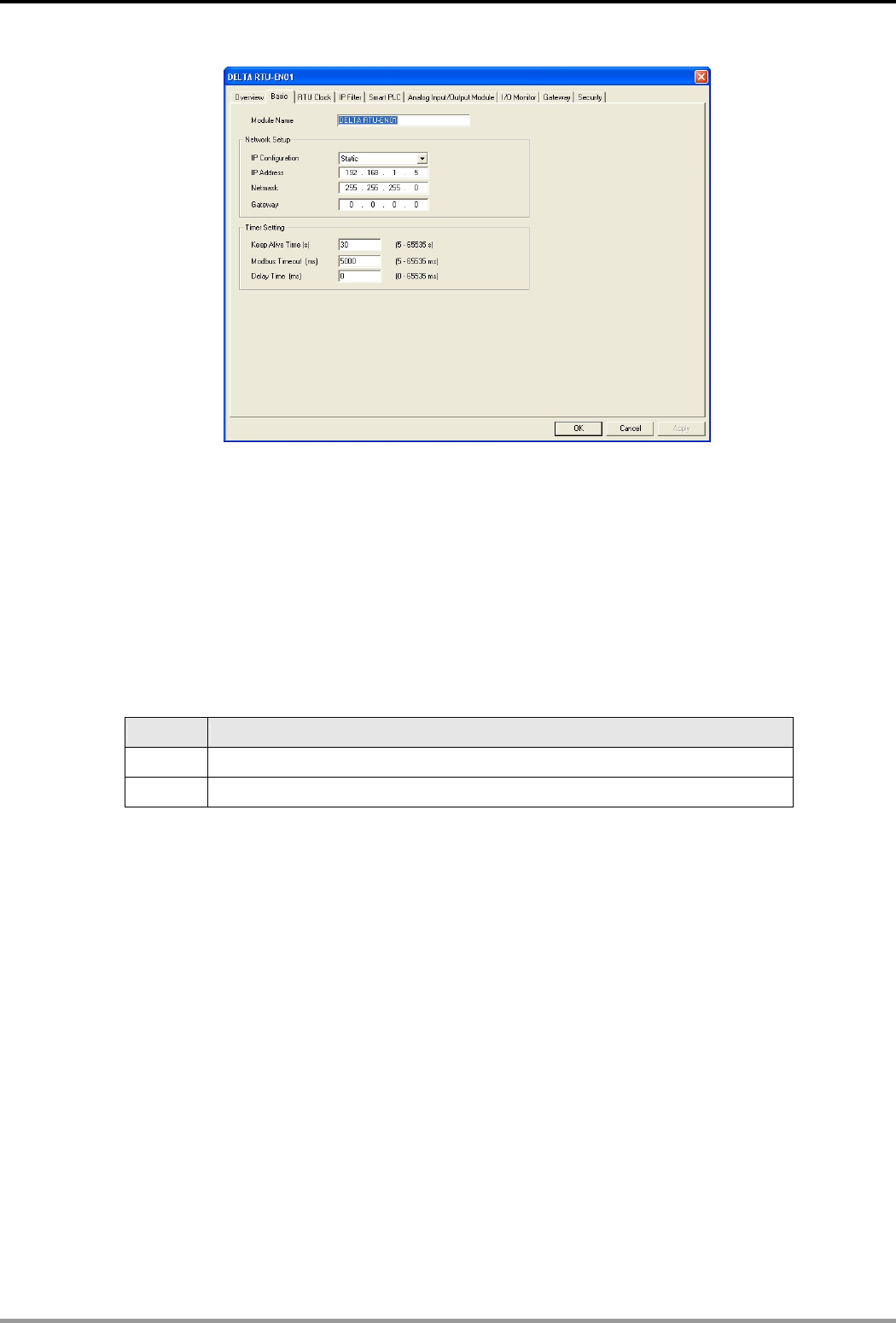
1. Module name:
There can be many RTU-EN01 modules on the network. Thus, you can set up a module name for each
module to identify the module when you need to use them.
2. Network setup:
Enable dynamic IP (DHCP) or static IP. Consult your ISP for other relevant settings.
A. IP configuration:
There are 2 types of IP, static IP and DHCP.
Static IP: Preset or manually modified by the user.
DHCP: Automatically updated by the server. There must be a server in the LAN.
IP Explanation
Static The user enters the IP address, subnet mask and gateway.
DHCP DHCP server offers the IP address, subnet mask and gateway.
B. IP address:
IP address is the location of the equipment on the network. Every equipment connected to the network
has to have an IP address. Incorrect IP address will result in connection failure. Consult your ISP for
how to set up IP address. The default IP for RTU-EN01 is 192.168.1.5.
C. Netmask:
Subnet mask is an important parameter for setting up the subnet, used for seeing if the destination IP
and the local equipment are in the same subnet. If not, the equipment will send the packet to the
gateway, and the gateway will send the packet to another subnet. Incorrect setting may cause the
destination equipment unable to communicate to RTU-EN01. To see if your setting is correct, conduct
bitwise AND operations between your IP and subnet mask and destination IP and subnet mask. If the
two values obtained are the same, the two IPs are in the same subnet. The default subnet mask of
RTU-EN01 is 255.255.255.0.
D. Gateway:
Gateway is the window for two different subnets, allowing the two ends in different subnets to
communicate. For example, if the LAN has to be connected to WAN, it will need a gateway to bridge