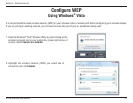
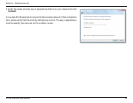
34D-Link DWA-556 User Manual
Section 4 - Wireless Security
WhatisWPA?
WPA, or Wi-Fi Protected Access, is a Wi-Fi standard that was designed to improve the security features of WEP (Wired Equivalent
Privacy).
The2majorimprovementsoverWEP:
•ImproveddataencryptionthroughtheTemporalKeyIntegrityProtocol(TKIP).TKIPscramblesthekeysusinga
hashing algorithm and, by adding an integrity-checking feature, ensures that the keys haven’t been tampered with.
WPA2 is based on 802.11i and uses Advanced Encryption Standard instead of TKIP.
•Userauthentication,whichisgenerallymissinginWEP,throughtheextensibleauthenticationprotocol(EAP).WEP
regulates access to a wireless network based on a computer’s hardware-specific MAC address, which is relatively
simple to be sniffed out and stolen. EAP is built on a more secure public-key encryption system to ensure that only
authorizednetworkuserscanaccessthenetwork.
WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK uses a passphrase or key to authenticate your wireless connection. The key is an alpha-numeric password
between 8 and 63 characters long. The password can include symbols (!?*&_) and spaces. This key must be the exact same key
entered on your wireless router or access point.
WPA/WPA2 incorporates user authentication through the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP). EAP is built on a more secure
publickeyencryptionsystemtoensurethatonlyauthorizednetworkuserscanaccessthenetwork.