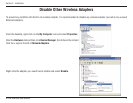
4D-Link DWA-556 User Manual
Section 1 - Product Overview
Introduction
The D-Link Wireless N™ Desktop Adapter (DWA-556) is a Draft 802.11n client device that delivers unrivaled wireless performance
for your desktop computer. With the DWA-556, you can add or upgrade your Desktop PC’s wireless connectivity without having to
purchase a new computer. Once connected, access your network’s high-speed Internet connection while sharing photos, files, music,
video, printers, and storage. Get a better Internet experience with a faster wireless connection so you can enjoy digital phone calls,
gaming, downloading, and video streaming.
Powered by Wireless N™ technology, the DWA-556 provides a faster wireless connection and superior reception than 802.11g*.
TheDWA-556isdesignedforuseinbiggerhomesandforthosethatdemandhighernetworking.Maximizewirelessperformanceby
connecting this desktop adapter to a Wireless N
™
Router and stay connected from virtually anywhere in the home. This adapter supports
WEP, WPA, and WPA2 encryption to prevent outside intrusion and protect your personal information from being exposed.
The D-Link Wireless N™ DWA-556 is a powerful 64-bit desktop adapter that installs quickly and easily into desktop computers. Like
all D-Link wireless adapters, the DWA-556 can be used in Ad Hoc mode to connect directly with other cards for peer-to-peer file
sharing or in infrastructure mode to connect with a wireless access point or router for access to the Internet in your office or home
network.
The DWA-556 features robust security to help protect the wireless network from intruders, complying with the latest wireless
networking security protocols, including WEP encryption and Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) support for WPA2-PSK. The DWA-
556 also includes a configuration utility to discover available wireless networks and create and save detailed connectivity profiles for
those networks most often accessed.
•
Maximum wireless signal rate derived from IEEE Standard 802.11g and draft 802.11n specifications. Actual data throughput will vary. Network conditions and environmental factors,
including volume of network traffic, building materials and construction, and network overhead, lower actual data throughput rate. Environmental factors will adversely affect wireless
signal range.