2–8 Planning and Design
Hitachi Simple Modular Storage Copy-on-Write SnapShot User’s Guide
5. Calculate the base data pool size for your primary/virtual volumes by
multiplying the MB size of one V-VOL in Step 4 by the number of V-VOLs,
which was established earlier. For example:
90,000 MB
x 4 V-VOLS = 360,000 MB
This is the base data pool size for a SnapShot system in which the copy
frequency is 1 hour, the copy lifespan is 4 hours, and the number of
copies (V-VOLs) is 4.
6. It is highly recommended that a safety factor of 20%, be calculated. Do
so using the following formula:
(Base data pool size) x 1.2. For example:
360,000 MB x 1.2 = 432,000 MB
7. It is also advisable to factor in annual increases in data transactions. Do
this by multiplying the base pool size by the percentage of expected
annual growth. For example:
432,000 MB x 1.2 (20 percent growth rate for per year)
= 518,400 MB
This is the size of the data pool with growth factored for the first year.
8. Repeat this step for each year the solution will be in place. For example:
518, 400 MB x 1.2 (20 percent growth rate for second year)
= 622,080 MB
This is the size of the data pool with growth factored for the second year.
Rule of Thumb Calculation
When measurements of host workload has not been performed, Hitachi
suggests the change rates shown in Table 2-1.
•
Data pool calculation using the suggested change rates in Table 2-1 is:
Data Pool size = (P-VOL x % of changed data x 2.5 safety rate)
x a number of V-VOLs
For example:
1. P-VOL = 1 TB. 1 snapshot per 24 hours. 25% of 1 TB = 250 GB.
2. Multiply the initial calculation by the Hitachi safety factor of 2.5. In the
example above: 2.5 x 250 GB = 625 GB. This is the base data pool size.
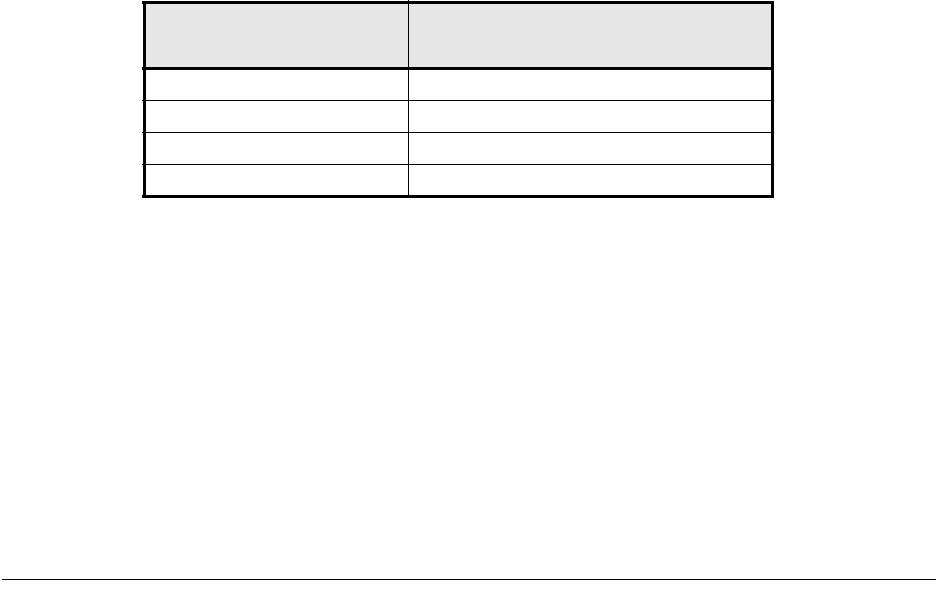
Table 2-1: Workload Rates when No Measurement
Snapshot lifespan
Suggested write workload
change rate
1-4 hours 10%
4-8 hours 15%
8-12 hours 20%
12-24 hours 25%