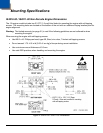
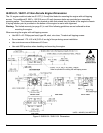
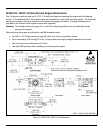
12
Theory of Operation
Overview
The IS4910 imaging engine series is specifically designed for integration into handheld portable data terminals
or other OEM devices used for barcode scanning and/or OCR applications. Since the imaging engine
functions like a digital camera, the engine is capable of digital image capture, document lift, and signature
capture. With software integration, the non-decode engine will support decoding of all standard 1D & 2D
barcodes, reading OCR.
The compact engine has a 1.2M pixel CMOS imaging sensor, high intensity illumination LEDs, and an LED
targeting system. The non-decode engine also incorporates FirstFlash
®
a patented technology that regulates
the illumination time during image capture, reducing the need for multiple image acquisition.
The IS4910 series has two types of imaging modes, the Snapshot mode and the Video mode. The Snapshot
mode facilitates fast and accurate image acquisition with a minimum amount of power consumption. In this
mode, the LEDs are only activated for a very short time while FirstFlash ensures proper illumination.
The amount of images required is minimized, ultimately reducing the engine's power consumption. Detailed
information on the Snapshot mode can be found on page 14. The second type, the Video mode, enables fine
control of the camera exposure time making the mode suitable for high ambient light applications. Detailed
information on the Video mode can be found on page 16.
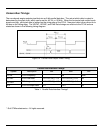
Communication with the image sensor is done over two buses, the control bus (I
2
C) and the data bus. The
Control bus is used to send programming commands to the image sensor. The data bus is used to transfer
images from the image sensor to the host system. The image data rate is determined by the Pixel Clock
(PCLK), which has a maximum frequency of 48 MHz. Note that on some host systems, such as those based
on the XScale PXA270 processor, the platform may not be able to support the 48 MHz pixel clock. In these
applications, the pixel clock can be configured to 24 MHz or 12 MHz via the (I
2
C) control bus. See Figure 9 on
page 13 for an illustrated depiction of the engine’s system architecture.