Chapter 6. System compatibility
3. Sends the EOI
4. Waits one I/O delay
5. Enables the interrupt through the Set Interrupt Enable Flag command
Hardware interrupt IRQ9 is defined as the replacement interrupt level for the cascade level IRQ2.
Program interrupt sharing is implemented on IRQ2, interrupt hex 0A. The following processing occurs to
maintain compatibility with the IRQ2 used by IBM Personal Computer products:
1. A device drives the interrupt request active on IRQ2 of the channel.
2. This interrupt request is mapped in hardware to IRQ9 input on the second interrupt controller.
3. When the interrupt occurs, the system microprocessor passes control to the IRQ9 (interrupt hex 71)
interrupt handler.
4. This interrupt handler performs an EOI command to the second interrupt controller and passes control
to the IRQ2 (interrupt hex 0A) interrupt handler.
5. This IRQ2 interrupt handler, when handling the interrupt, causes the device to reset the interrupt
request before performing an EOI command to the master interrupt controller that finishes servicing
the IRQ2 request.
Diskette drives and controller
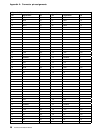
The following figures show the reading, writing, and formatting capabilities of the diskette drive.
Copy protection The following methods of copy protection might not work in systems using the 3.5-inch
1.44 MB diskette drive.
Bypassing BIOS routines
– Data transfer rate: BIOS selects the proper data transfer rate for the media being used.
– Diskette parameter table: Copy protection, which creates its own diskette parameter table, might
not work in these drives.
Diskette drive controls
– Rotational speed: The time between two events in a diskette drive is a function of the controller.
– Access time: Diskette BIOS routines must set the track-to-track access time for the different types
of media that are used in the drives.
– ‘Diskette change’ signal: Copy protection might not be able to reset this signal.
Write-current control: Copy protection that uses write-current control does not work, because the
controller selects the proper write current for the media that is being used.
Hard disk drives and controller
Reading from and writing to the hard disk is initiated in the same way as in IBM Personal Computer
products; however, new functions are supported.
Figure 17. 3.5-inch diskette drive reading, writing, and formatting capabilities
Diskette drive type 720 KB Mode 1.44 MB Mode
1.44 MB drive RWF RWF
2.88 MB drive RWF RWF
Chapter 6. System compatibility 23