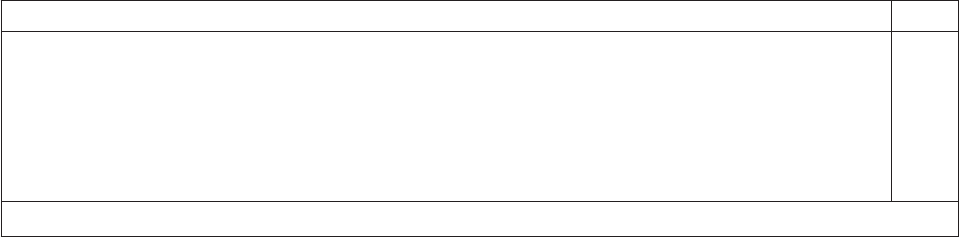
Modified /boot/grub/menu.lst contents Notes
root
chainloader +1
title failsafe
kernel (hd0,1)/boot/vmlinuz.shipped root=/dev/hda2 ide=nodma apm=off vga=normal nosmp 1
disableapic maxcpus=0 3
initrd (hd0,1)/boot/initrd.shipped
Note 1: The kernel line is shown with a line break. In your file, the entire entry must all be on one line.
You must restart the Linux operating system after completing these procedures for
the changes to take effect and to enable SOL.
Microsoft Windows 2003 Standard Edition configuration
Note: This procedure is based on a default installation of the Microsoft Windows
2003 operating system.
Complete the following steps to configure the Windows 2003 operating system for
SOL operation. You must be logged in as a user with administrator access to
perform this procedure.
1. Complete the following steps to determine which boot entry ID to modify:
a. Type bootcfg at a Windows command prompt; then, press Enter to display
the current boot options for your server.
b. In the Boot Entries section, locate the boot entry ID for the section with an
OS friendly name of Windows Server 2003, Standard. Write down the boot
entry ID for use in the next step.
2.
To enable the Microsoft Windows Emergency Management System (EMS), at a
Windows command prompt, type
bootcfg /EMS ON /PORT COM1 /BAUD 19200 /ID boot_id
where boot_id is the boot entry ID from step 1b; then, press Enter.
3. Complete the following steps to verify that the EMS console is redirected to the
COM2 serial port:
a. Type bootcfg at a Windows command prompt; then, press Enter to display
the current boot options for your server.
b. Verify the following changes to the bootcfg settings:
v In the Boot Loader Settings section, make sure that redirect is set to
COM2 and that redirectbaudrate is set to 19200.
v In the Boot Entries section, make sure that the OS Load Options: line
has /redirect appended to the end of it.
The following examples show the original bootcfg program output and the output
after modification.
Chapter 2. Configuring the server 31


















