Overview of IBM Networking
DLSw+
BC-212
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
If you are using NetBIOS applications, note that there are two NetBIOS timers—one at the link level
and one at the next higher level. Local acknowledgment for LLC2 is designed to solve link timeouts only.
If you are experiencing NetBIOS session timeouts, you have two options:
• Experiment with increasing your NetBIOS timers and decreasing your maximum NetBIOS frame
size.
• Avoid using NetBIOS applications on slow serial lines.
Note By default, the Cisco IOS software translates Token Ring LLC2 to Ethernet 802.3 LLC2.
To configure the router to translate Token Ring LLC2 frames into Ethernet 0x80d5 format
frames, refer to the section “Enable Token Ring LLC2-to-Ethernet Conversion” in the
“Configuring Source-Route Bridging” chapter of the Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM
Networking Command Reference, Volume I.
DLSw+ Support for Other SNA Features
DLSw+ can be used as a transport for SNA features such as LAN Network Manager (LNM), DSPU, SNA
service point, and SNA Switching Services (SNASw) through a Cisco IOS feature called virtual
data-link control (VDLC).
LNM over DLSw+ allows DLSw+ to be used in Token Ring networks that are managed by IBM’s LNM
software. Using this feature, LNM can be used to manage Token Ring LANs, control access units, and
Token Ring attached devices over a DLSw+ network. All management functions continue to operate as
they would in a source-route bridged network or an RSRB network.
DSPU over DLSw+ allows Cisco’s DSPU feature to operate in conjunction with DLSw+ in the same
router. DLSw+ can be used either upstream (toward the mainframe) or downstream (away from the
mainframe) of DSPU. DSPU concentration consolidates the appearance of multiple physical units (PUs)
into a single PU appearance to VTAM, minimizing memory and cycles in central site resources (VTAM,
NCP, and routers) and speeding network startup.
SNA service point over DLSw+ allows Cisco’s SNA service point feature to be used in conjunction with
DLSw+ in the same router. Using this feature, SNA service point can be configured in remote routers,
and DLSw+ can provide the path for the remote service point PU to communicate with NetView. This
allows full management visibility of resources from a NetView 390 console, while concurrently offering
the value-added features of DLSw+ in an SNA network.
SNASw over DLSw+ allows Cisco’s APPN Branch Extender functionality to be used in conjunction with
DLSw+ in the same router. With this feature, DLSw+ can be used to access SNASw in the data center.
DLSw+ can also be used as a transport SNASw upstream connectivity, providing nondisruptive recovery
from failures. The DLSw+ network can appear as a connection network to the SNASw nodes.
Using DLSw+ as a transport for other Cisco IOS SNA features requires a feature called VDLC. Cisco
IOS data-link users (such as LNM, DSPU, SNA service point, and SNASw) write to a virtual data-link
control interface. DLSw+ then reads from this interface and sends out the traffic. Similarly, DLSw+ can
receive traffic destined for one of these Data Link Users and write it to the virtual data-link control
interface, from which the appropriate Data Link User will read it.
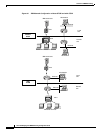
In Figure 88, SNASw and DLSw+ use Token Ring and Ethernet, respectively, as “real” data-link
controls, and use virtual data-link control to communicate between themselves. When one of the
high-layer protocols passes data to the virtual data-link control, the virtual data-link control must pass
it to a higher-layer protocol; nothing leaves the virtual data-link control without going through a
data-link user.