Overview of IBM Networking
Cisco Transaction Connection
BC-244
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
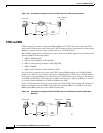
Figure 109 Cisco Router Configured with the CTRC Feature for CICS Communications
CTRC and DB2
CTRC enables Cisco routers to implement IBM’s DRDA over TCP/IP. The Cisco router with CTRC
exists in the TCP/IP network, and clients use a CTRC IP address and port on the router to connect to the
IBM host system that exists in either an SNA network or a TCP/IP network.
When CTRC is appropriately configured on a router, client-based ODBC applications can connect to the
following IBM D2 relational databases:
• DB2 for OS/390 (MVS)
• DB2 for Virtual Machine (VM) (SQL/DS)
• DB2 for Virtual Storage Extended (VSE) (SQL/DS)
• DB2 for OS/400
• DB2 Universal Database (UNIX, Windows, OS/2)
For an SNA host connection, the router with CTRC converts DRDA packets over TCP/IP to DRDA
packets over (APPC LU 6.2) and then routes them to DB2 databases. CTRC runs as a TCP/IP daemon
on the router, accepting DRDA client connections over TCP/IP. When a client connects to the database
on an IBM mainframe host, CTRC allocates an APPC conversation over SNA to an IBM server, and acts
as a gateway between DRDA over TCP/IP and DRDA over APPC.
Figure 110 illustrates how the Cisco router configured with the CTRC feature enables the exchange of
database information between ODBC client applications running DRDA in a TCP/IP network and a
DRDA-based IBM system that accesses DB2 relational data.
Figure 110 Cisco Router Configured with the CTRC Feature for DB2 Communications (SNA Host
Network)
CTRC
TCP/IP SNA
TCP/IP
CICS transaction
monitor
26062
SNA
SNA
APPC
(LU 6.2)
CICS client
TCP/IP
CTRC
TCP/IP SNA
TCP/IP
DRDA server
DB2 database
26076
RDBMS
SNA
SNA
APPC
(LU 6.2)
ODBC client
TCP/IP