Overview of IBM Networking
NCIA
BC-230
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
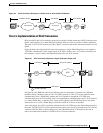
Figure 101 NCIA Server Client/Server Model
NCIA Data Link Control (NDLC) is the protocol used between clients and servers. NDLC serves two
purposes:
• Establishes the peer connection
• Establishes the circuit between the client and the server
The peer session must be established before an end-to-end circuit can be set up. During the set up period
for the peer session, the MAC address representing a client is defined. The MAC address can be defined
by the client or by the server when the client does not have a MAC address.
The NCIA Server feature supports connect-in and connect-out (from the server’s perspective), but
connect-out is not supported if the client station does not listen for the incoming connection. For a server
to connect-out, clients must connect to the server first. After registering itself by providing its own MAC
address, the client can then optionally disconnect from the server. When a server receives an explorer,
and its destination MAC address is registered, an NCIA server will connect to that client if it is not
connected. For NetBIOS explorers (addressed to functional address 0xC00000000080), the TCP session
must remain up so that the server can broadcast the explorers to the client. If the TCP session is down,
the server will not send the NetBIOS explorers to a client, even when the client is registered.
After the peer session has been established, the NDLC protocol establishes the circuit between the client
and server. This circuit is used to transfer end-user data between the client and the server. Because the
client and its target station are not on the same transport, they cannot form a direct, end-to-end circuit.
Each client must form a circuit between the client and server, and the server must form another circuit
between the server and the target station. The server links those two circuits to form an end-to-end
circuit. The server acts as a mediator between the client and the target station so that packets can be
transferred between them.
In the NCIA server only peer keepalive is maintained. There is no keepalive at circuit level.
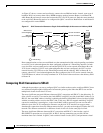
The NCIA server acts as a data-link provider, like Token Ring or Ethernet, in the router. It uses CLSI to
communicate with other software modules, just as other data-link providers do. The network
administrator configures the router to communicate with specific modules. For data-link users, such as
SNASw, DLSw+, and DSPU, the NCIA server can interface to them directly. For other data-link
providers, the NCIA server must go through a DLSw+ local peer to communicate with them. The
DLSw+ local peer passes packets back and forth among different data-link providers.
S4696
LLC2
SNASw
Ethernet Token Ring
TCP/IP TCP/IP
NCIA Server RSRB
NDLC
DLSw+ DLSw local switch DSPU
NCIA Client
SNA