Overview of IBM Networking
HPR Capable SNA Routing Services
BC-237
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
HPR Capable SNA Routing Services
SNASw provides the following SNA routing functions:
• Routes SNA sessions between clients and target SNA data hosts.
• Supports full SNA class of service (COS) features.
• Controls SNA traffic in a multiprotocol environment in conjunction with other Cisco IOS quality of
service (QOS) features.
• Supports networks with a high proportion of SNA traffic and multiple enterprise servers, especially
those that continue to support the traditional SNA endstation platform and new client types.
• Supports all types of SNA application traffic including traditional 3270 and peer LU 6.2.
• Supports an OS/390 Parallel Sysplex configuration, working in conjunction with the IBM
Communications Server for S/390 (formerly VTAM) and the MVS Workload Manager, to provide
higher availability in the data center using the High Performance Routing (HPR) feature.
• Supports System Services Control Point (SSCP) services to downstream SNA devices using the
Dependent LU Requester (DLUR) feature.
• Provides dynamic link connectivity using connection networks (CNs), which eliminates much of the
configuration required in networks with numerous data hosts.
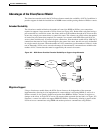
Branch Extender
The BEX function enhances scalability and reliability of SNA routing nodes by eliminating topology
updates and broadcast directory storms that can cause network instability. BEX appears as an NN to
downstream EN, LEN node, and PU devices, while also appearing as an EN to upstream devices. The
BEX function eliminates APPN topology and APPN broadcast search flows between SNASw nodes and
the SNA data hosts in the network. This feature is key to providing a reliable turn-key installation
because the network administrator no longer needs to develop in-depth knowledge of the level and
characteristics of broadcast directory search and topology update traffic in the network. Such knowledge
and analysis was commonly required to build successful networks utilizing NN technology without
BEX.
SNA Switching Services enables BE functionality by default. SNASw treats all defined links as BE
“uplinks” and all dynamic links created by stations connecting into SNASw as BE “downlinks.” No
specific configuration is necessary to enable BE functionality.
Figure 107 illustrates the BX functionality.