RAID Configuration
Page 5-1
Section 5
RAID CONFIGURATION
Introduction
This section gives a brief introduction on RAID-related background knowledge and
a general procedure to setup RAID system on this mainboard.
RAID Basics
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a method of combining two or
more hard disk drives into one logical unit known as a RAID array. The advantage
of RAID is to provide better performance or data fault tolerance. Fault tolerance is
achieved through data redundant operation, where if one drives fails, a mirrored
copy of the data can be found on another drive. This can prevent data loss if the
operating system fails or hangs.
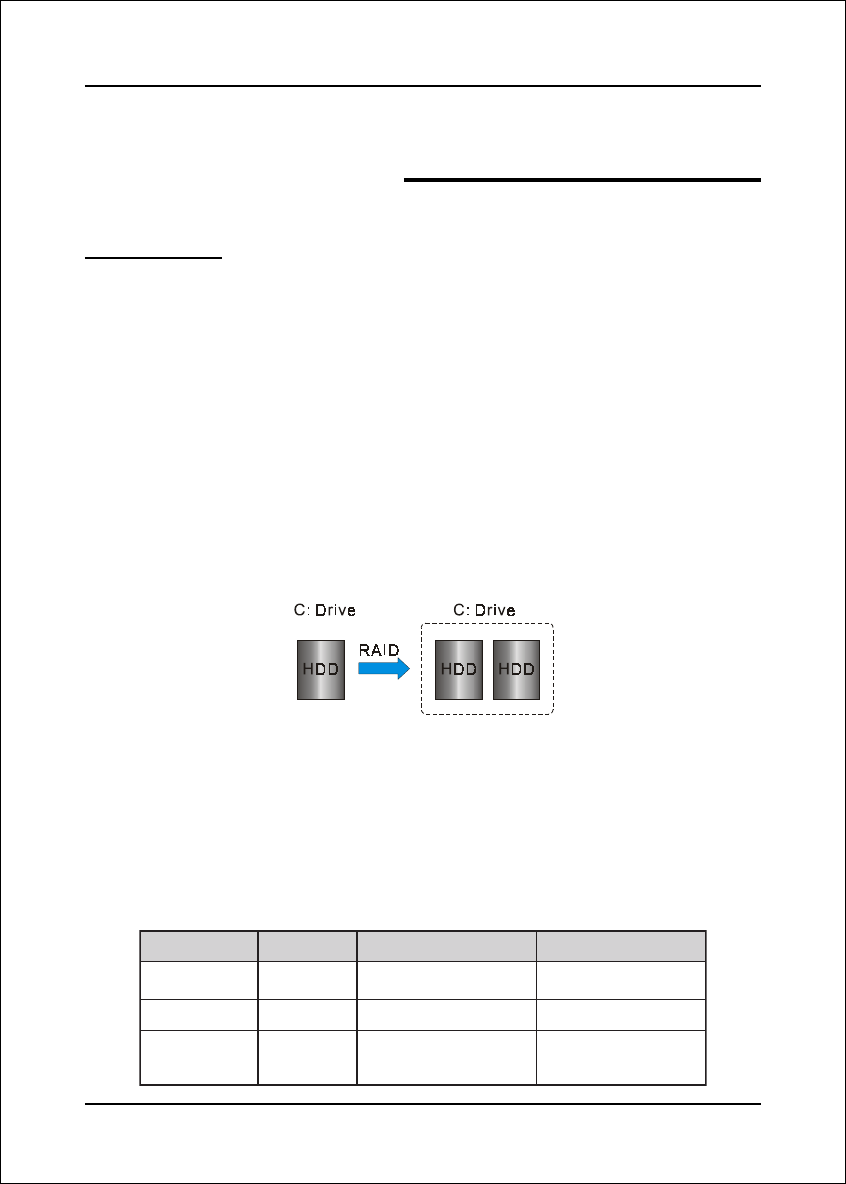
Below is an example of a RAID array with 2 drives.
The individual disk drives in an array are called “members”. All disk members in a
formed disk array are recognized as a single physical drive to the operating system.
Hard disk drives can be combined together through a few different methods. The
different methods are referred to as different RAID levels. Different RAID levels
represent different performance levels, security levels and implementation costs.
The table below briefly introduce these RAID levels.
leveLDIAR sevirDfo.oN yticapaC stifeneB
)gnipirtS(0DIAR2 ezistsellamS*srevirdrebmuN
tuohtiwecnamrofreptsehgiH
noitcetorpatad
)gnirorriM(1DIAR2ezistsellamSnoitcetorpataD
)gninnapS(DOBJ2srevirdllAfomuS
dnanoitcetorpatadoN
tub,gnivorpmiecnamrofrep
.desuyllufyticapacksid


















