37
Chapter 5: Using the Wireless Network Monitor
Creating a New Profile
Compact Wireless-G USB Adapter
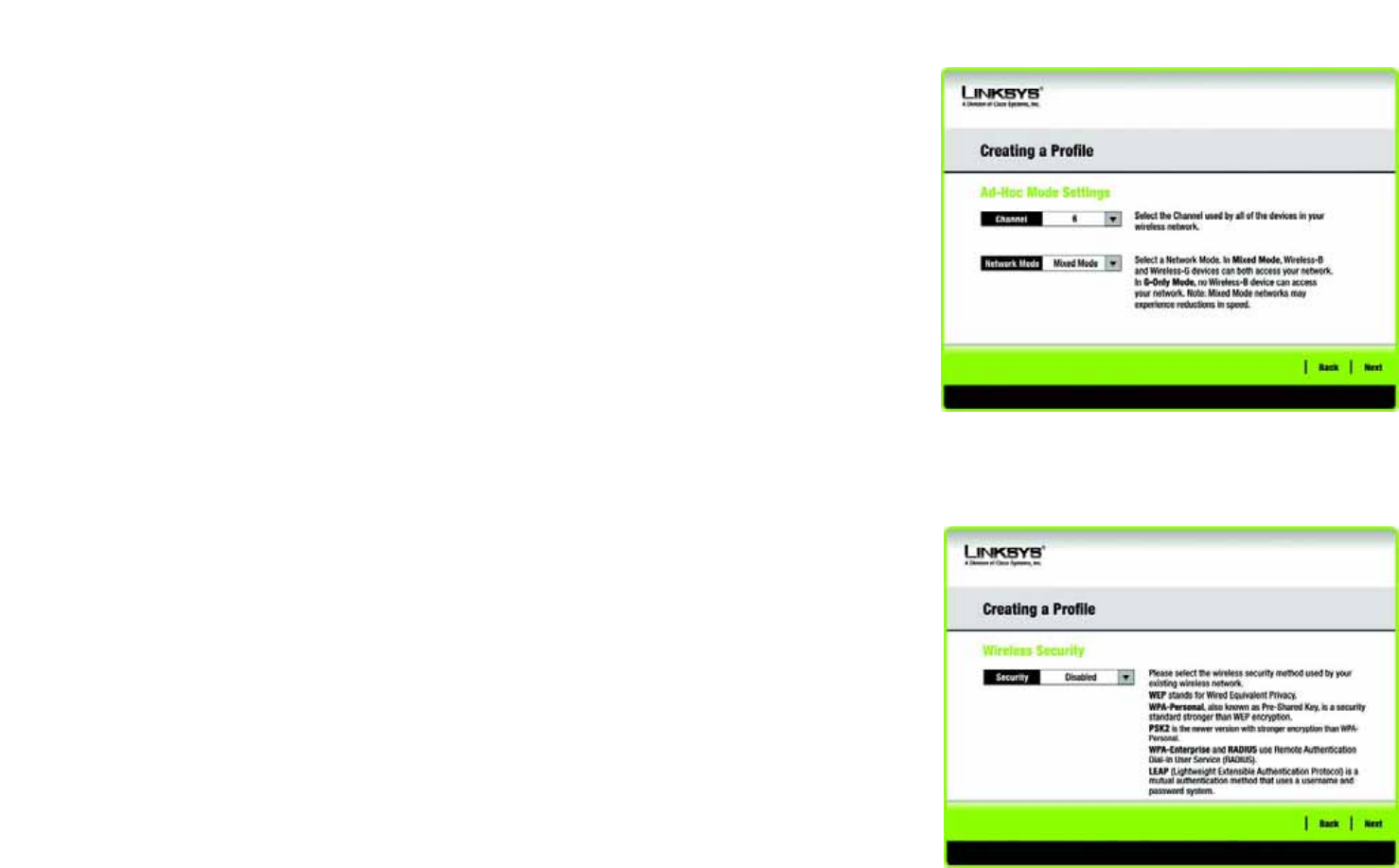
3. If you chose Infrastructure Mode, go to Step 4 now. If you chose Ad-Hoc Mode, the Ad-Hoc Mode Settings
screen will appear.
Select the correct Channel for your wireless network. The channel you choose should match the channel set
on the other devices in your wireless network. If you are unsure about which channel to use, keep the default
setting.
Then, select the Network Mode in which your wireless network will operate. In Mixed Mode, Wireless-B and
Wireless-G devices can both operate on the network, though at a slower speed. In G-Only Mode, no Wireless-
B devices can operate in the network.
Click Next to continue or click Back to change any settings.
4. The Wireless Security screen will appear. This step will configure wireless security.
If your wireless network doesn’t use wireless security, select Disabled and then click the Next button to
continue. Proceed to Step 6.
Select WEP, WPA-Personal, PSK2, WPA Enterprise, Radius, or LEAP for the Encryption Method. WEP
stands for Wired Equivalent Privacy, WPA stands for Wi-Fi Protected Access, which is a security standard
stronger than WEP encryption, PSK2 stands for Pre-Shared Key 2, which is a security standard stronger than
WPA-Personal, RADIUS stands for Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service, and LEAP stands for
Lightweight Extensible Authentication Protocol. If you don’t want to use encryption, select Disabled.
Figure 5-30: Ad-Hoc Mode Settings
Figure 5-31: Wireless Security


















