RAIDBank4 Owner’s Manual
63
SCSI acronym for “Small Computer System Interface”, SCSI is a set of standards for physically
connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. The SCSI standards
define commands, protocols, and electrical and optical interfaces. SCSI is most commonly used for
hard disks and tape drives, but it can connect a wide range of other devices, including scanners
and CD drives. Most modern storage protocols are based on the SCSI Block Protocol.
Secondary Storage Mass storage devices such as hard disks, magneto-optical disks, floppy
disks and tapes are frequently referred to as secondary storage.
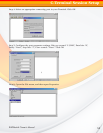
Stripe A stripe is a logical space that spans across multiple hard disks with each constituent
hard disk contributing equal strips (or chunks) of space to the stripe. In the figure below,
strips 1, 2, and 3 from hard disk 1, 2, and 3 respectively comprise a (purple colored) stripe.
Synonym: majorstripe
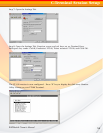
Stripe Set A stripe set is a set of stripes that spans across multiple hard disks. In the figure
below, the displayed stripe set has 4 stripes, with strip number 1 comprised of the purple
strips 1A, 1B and 1C. Stripe number 2 is comprised of the green strips 2A, 2B and 2C etc.
Stripe Size This is the size of the strips that constitute each stripe. This term is a misnomer
– though prevalent – since it should appropriately be called strip size or chunk size.
TCP/IP This is an acronym for “Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol”. It is
comprised of two parts TCP and IP. The former, i.e., TCP is a peer-to-peer connection oriented
protocol that guarantees the delivery of data packets in the correct sequence between two
peers. The latter, i.e., IP is the protocol that defines and governs addressing, fragmentation,
reassembly and time-to-live parameters for packets.
Volume Set A volume set is a concatenation of storage elements that may be RAID arrays,
JBODs, or simply areas of disks that are not part of RAID arrays.
Write-back Cache a caching scheme that acknowledges the write request as complete before
data is written to the final storage location. This methodology can improve the efficiency
of write operations under favorable circumstances, but is at risk of data incoherencies in a
system that is not protected from power fluctuations or failures.
Write-through Cache When a cache is operating in write-through mode, data written into the
cache is also written to the destination secondary storage devices. Essentially write completion
does not occur until the data is written to secondary storage. Thus the contents of the cache
and the secondary storage are always consistent. The advantage is that the possibility of data
corruption is greatly reduced. The disadvantage is that write-through operations are more time
consuming
XOR Function All RAID arrays (with the exception of RAID 0, RAID 1 and RAID 10) require
paritytobecalculatedandwrittentothearrayinconjunctionwithdata.Typicallytheparityis
a simple XOR on the bytes comprising a stripe. This is a computationally intensive operation
that many modern RAID controllers perform using a dedicated ASIC often referred to as a
XOR-engine.
D-Glossary