28
Service Set Identification (SSID)
The Service Set Identification (SSID) is a thirty-two alphanumeric character (maximum) string
identifying the wireless local area network. Some vendors refer to the SSID as network name. For
stations to communicate with each other, all stations must be configured with the same SSID.
A wireless LAN consisting of nodes operating in ad-hoc configuration without an access point is
called a Basic Service Set (BSS). All nodes in a BSS must use the same Basic Service Set ID
(BSSID).
In an infrastructure configuration with access points, multiple BSS can be configured to form an
Extended Service Set (ESS). In this configuration, the access points are configured with the same
Extended Service Set ID (ESSID). Wireless clients configured with the same ESSID can freely roam
from one Access Point domain to another and still maintain seamless connection to the network
Authentication and WEP Encryption
The absence of a physical connection between nodes makes the wireless links vulnerable to
information theft. To provide a certain level of security, IEEE 802.11 standard has defined two types
of authentication methods, Open System and Shared Key. Open System authentication is a null
algorithm. Shared Key authentication is an algorithm where both the transmitting node and the
receiving node share an authentication key to perform a checksum on the original message. By
default, IEEE 802.11 wireless devices operate in an open system network.
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) data encryption is utilized when the wireless nodes or access
points are configured to operate in Shared Key authentication mode. There are two shared key
methods implemented in most commercially available products, 40-bit WEP data encryption and
128-bit WEP data encryption.
The 40-bit WEP data encryption method, allows for a five-character (40-bit) input. Additionally, 24
factory-set bits are added to the 40-bit input to generate a 64-bit encryption key. (The 24 factory-set
bits are not user configurable.) This encryption key will be used to encrypt/decrypt all data
transmitted via the wireless interface. Some vendors may refer to the 40-bit WEP data encryption
as 64-bit WEP data encryption since the actual encryption key used in the encryption process is 64
bits wide.
The 128-bit WEP data encryption method consists of 104 configurable bits. Similar to the 40-bit
WEP data encryption method, the remaining 24 bits are factory set and not user configurable. Some
vendors allow passphrases to be entered instead of the cryptic hexadecimal characters to ease
encryption key entry.
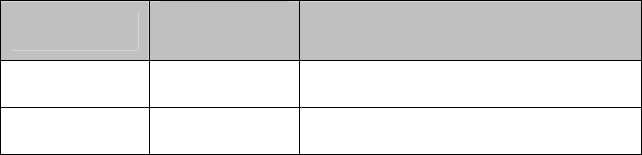
Encryption Key
Size
# of
Hexadecimal
Digits
Example of Hexadecimal Key Content
64-bit
(24+40)
10 4C72F08AE1
128-bit
(24+104)
26 4C72F08AE19D57A3FF6B260037