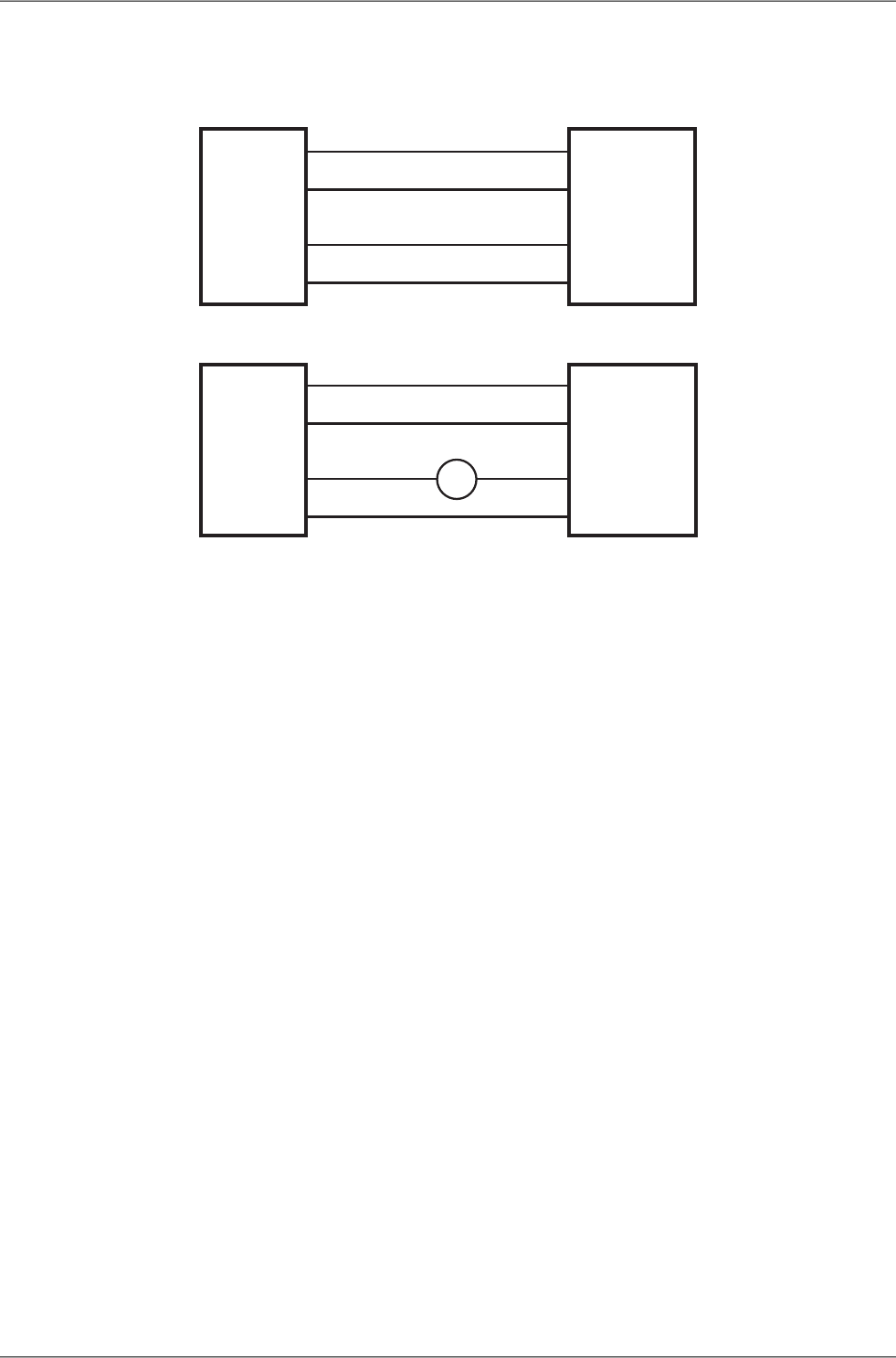
Analog outputs 0 and 1 have connected terminals - (minus), which are galvanically separated from the
modem GND.
-A in
-A in
+A in
+A in
-A out
-A out
+A out
+A out
-A out
-
+A out
+
-A in
-
+A in
+
=
-
+
voltagesupply
MR400
MR400
MR400 or
technology
withanactive
currentloop
transmitter
technology,
passive
current
loop
transmitter
Fig. 3.7: Examples of wiring analog inputs and outputs
The MR400 radio modem used in the diagram showing examples of wiring can, of course, be replaced
by any MORSE system modem. (e.g. MD160, MX 160, MWxxx, MRxxx, MC100, ...)
3.5. M-BUS module
(Meter-Bus)
Use
The M-BUS board serves as the MASTER interface of the physical layer of the M-BUS for the application
of data collection from meters regulating the consumption of various types of media (water, gas, heat,
etc.).
A M-BUS module can be positioned in the first or second slot of optional modules, see section Sec-
tion 3.11, “View of Radio Modem”. (For MG100 only in the first slot.) The second slot is recommended
because when using slot 1 you first need to disconnect it in the modem´s service mode, see section
Section 3.10, “Service Connector”.
For the correct operation of the module it needs to be configured to the proper SCC in menu SPe using
Setr:
dia(g) mode : NORM
pr(o)tocol : L&G 870-5-2 IEC
Wideband modems – PROFI MX160 – © RACOM s.r.o.14
Connectors