4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
10
2 INTRODUCTION TO RAID
2.1 RAID VOLUMES
RAID technology allows one or more disks to be combined into a logical volume which
provides greater performance and/or protection than standard disk drives. These volumes,
also known as RAID Groups, appear like regular disk drives to the operating system and can
be partitioned, formatted and used just like any other normal disk. The complexity of the RAID
is hidden within the driver.
There are several different methods of combining disks, each with its own advantages and
disadvantages. Each method is referred to as a RAID “level” such as RAID 1, or RAID 5. The
details of each level are summarized below and detailed in the following sections.
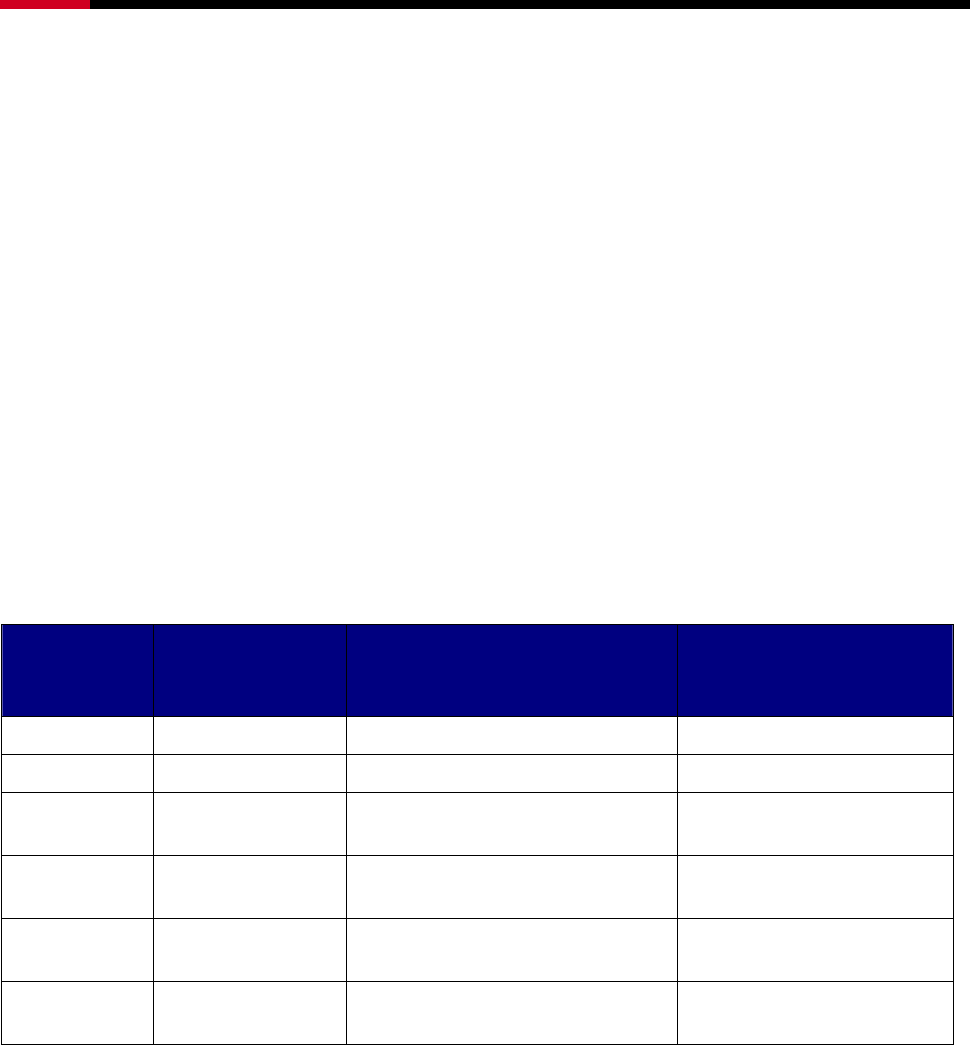
RAID LEVEL CONFIGURED
AS
ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES
0 Striped Excellent performance, low cost No data protection
1 Mirrored Excellent data protection High cost
10 Mirrored Striped
High performance, excellent
data protection.
High cost.
5 Parity RAID
Good data protection, good
value
Some performance
degradation for writes.
Combination Concatenated
Good performance, low cost,
large Volume size
No data protection
Single Drive /
Segment
Contiguous Same as single disk Same as single disk
2.2 SEGMENTING DISKS
For increased versatility, the SATARAID5 software allows individual disks to be divided into
smaller segments which can then be combined into different volumes. As an example, if a
user has one set of data that must be protected at all costs, another set of data which should
be protected at reasonable cost and another set that doesn’t need any protection at all; the
user can divide three disks into sections as shown in Figure 1. The yellow regions define the


















