4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
13
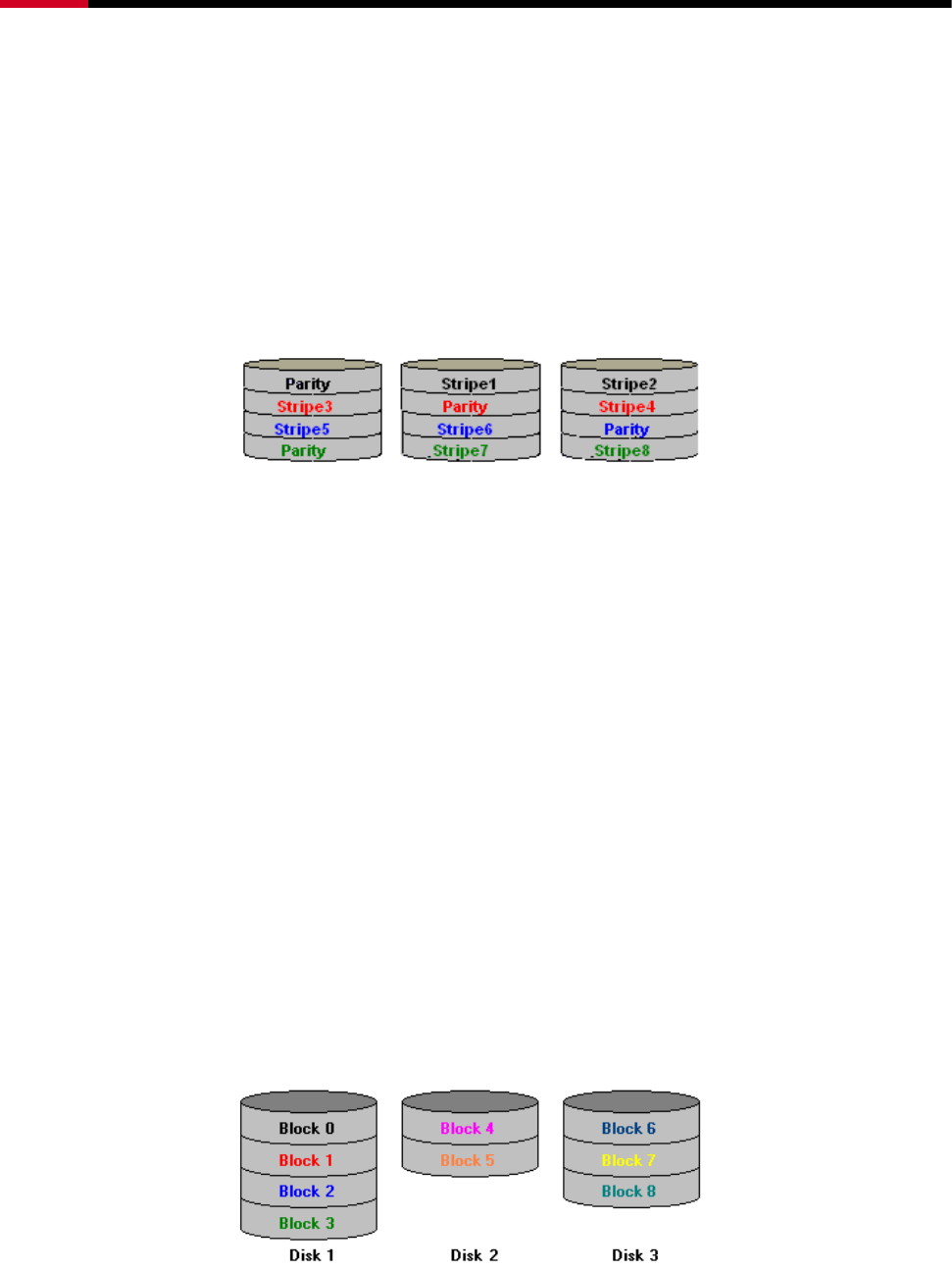
2.3.4 PARITY RAID (RAID 5)
Parity or RAID 5 adds fault tolerance to Disk Striping by including parity information with the
data. Parity RAID dedicates the equivalent of one disk for storing parity stripes. The data and
parity information is arranged on the disk array so that parity is written to different disks.
There are at least 3 members to a Parity RAID set. The following example illustrates how the
parity is rotated from disk to disk. The following example illustrates how the parity is rotated
from disk to disk.
Parity RAID uses less capacity for protection and is the preferred method to reduce the cost
per megabyte for larger installations. Mirroring requires 100% increase in capacity to protect
the data whereas the above example using three hard drives only requires a 50% increase.
The additional required capacity decreases as the number of disks in the group increases (i.e.,
33% for four drives or 25% for five drives).
In exchange for low overhead necessary to implement protection, Parity RAID degrades
performance for all write operations. The parity calculations for Parity RAID may result in write
performance that is somewhat slower than the write performance to a single disk.
2.3.5 CONCATENATION
The Concatenated mode combines multiple disks or segments of disks into a single large
volume. It does not provide any data protection or performance improvement but can be
useful for utilizing leftover space on disks. Concatenation allows the segments that make up
the volume to be of different sizes.


















