Abstract
The HP BladeSystem c3000 Enclosure is the next generation in an evolution of the entire rack-
mounted infrastructure. The c3000 enclosure is designed for remote sites, small and medium-sized
businesses, and data centers with special power and cooling constraints. This technology brief
provides an overview of the HP BladeSystem c3000 Enclosure, Thermal Logic power and cooling
technologies, and interconnect options.
This technology brief assumes the reader is familiar with HP ProLiant server technology and has some
knowledge of general BladeSystem architecture. For more information about the infrastructure
components, see the HP website at
www.hp.com/go/bladesystem/.
Overview of HP BladeSystem c3000 Enclosure
The HP BladeSystem c3000 Enclosure, announced in September 2007, is the newest enclosure
implemented using the BladeSystem c-Class architecture. While the c7000 enclosure is optimized for
enterprise data center applications, the c3000 enclosure is optimized for other computing
environments such as remote sites or small businesses. More information on c-Class architecture and
the c7000 enclosure is available on the HP technology website at
www.hp.com/servers/technology.
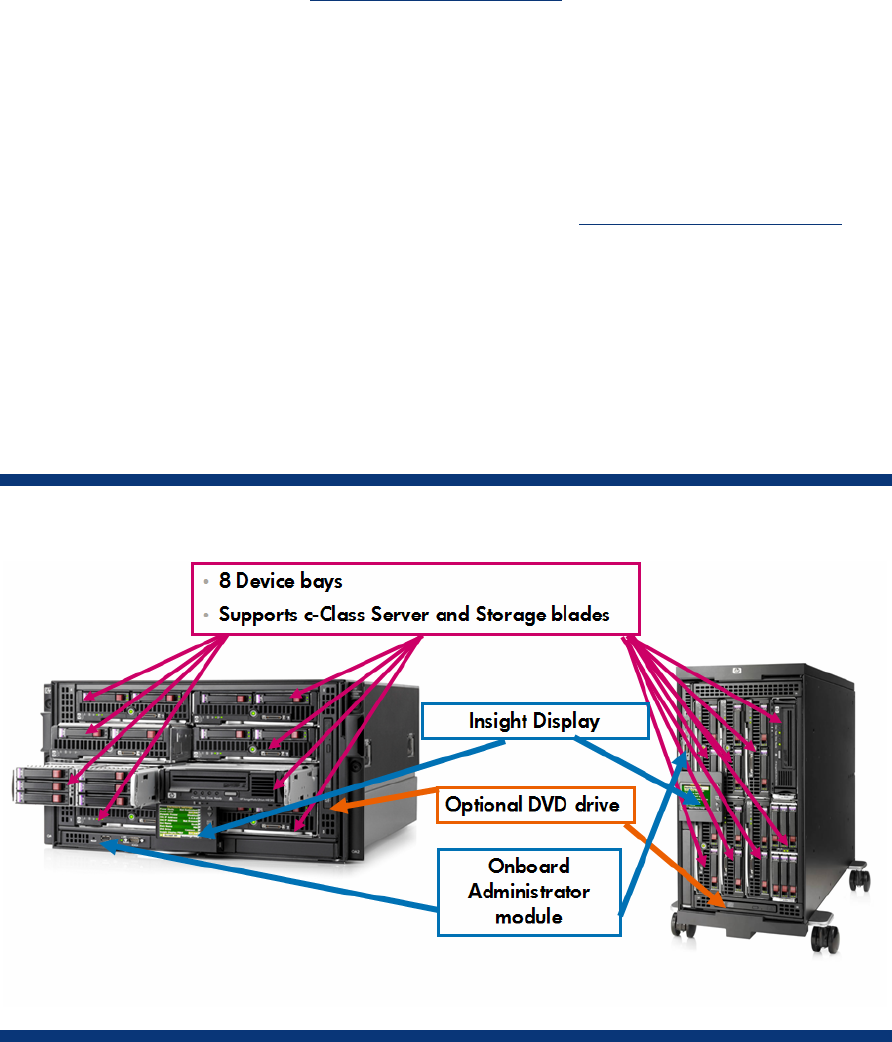
The c3000 enclosure is available in two different models, the c3000 rack model that fits into standard
size HP and third-party racks, and the c3000 Tower model, which works well in sites without racks
(Figures 1 and 2). Both models employ c-Class form-factor server blades, storage blades, and
interconnect modules. The c3000 enclosure is optimized for particular computing environments such
as remote sites, retail stores, small offices, oil platforms, ships, planes, trucks, or any site with limited
power options. The c3000 enclosure is also designed for sites that may not have any special cooling
capability, and can exist in environments of up to 35 degrees centigrade. The c3000 enclosure is
designed for use with management devices such as local KVM switches for local administration.
Figure 1. HP BladeSystem c3000 Enclosure – front view
3


















