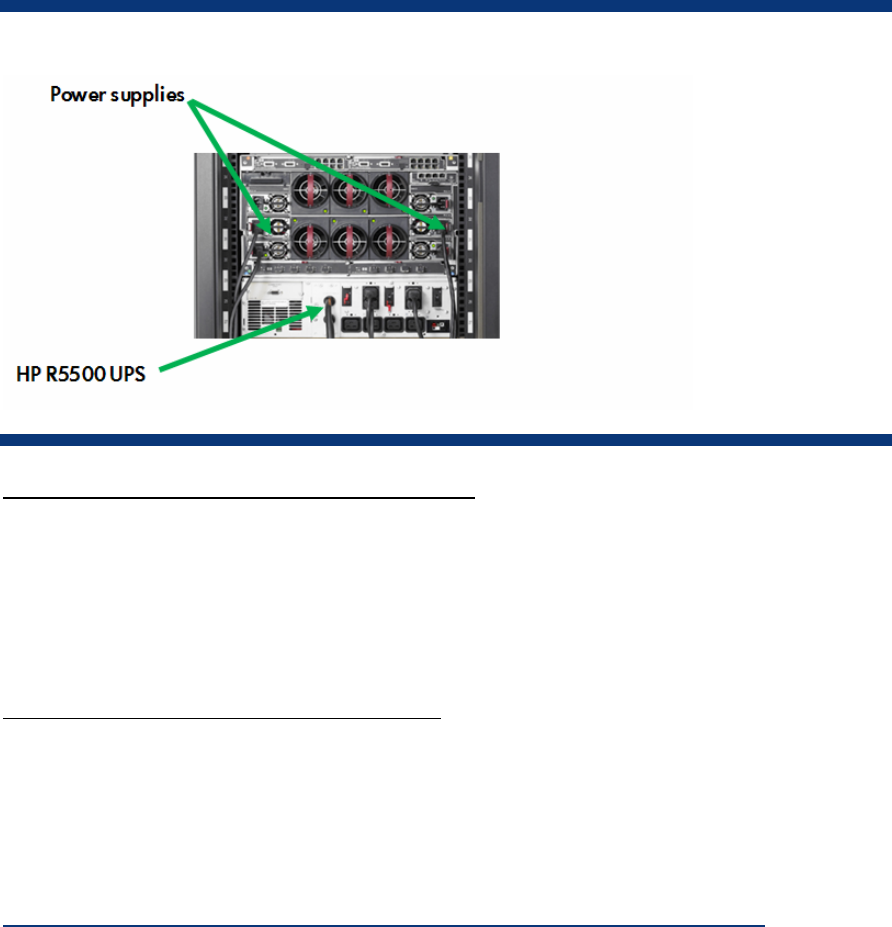
Figure 21. Redundant HP BladeSystem c3000 power supplies connected to an HP R5500 UPS
Connecting to PDUs with AC redundancy to each rack
In an N+N AC redundancy configuration, the total power available in the power pool equals the
amount from the A or B side, whichever contains fewer power supplies. In this configuration, N power
supplies are used to provide power, and the same number are used to provide redundancy. N can
equal 1, 2, or 3. Any number of power supplies from 1 to N can fail without causing the enclosure to
lose power. When correctly wired with redundant AC line feeds, this configuration will also ensure
that a single AC line feed failure will not cause the enclosure to power off.
Connecting with no power redundancy configured
In a configuration with no power redundancy, the total power available in the power pool equals the
sum of the power generated by all installed power supplies. Any power supply failure will cause the
system to power off if the remaining power supplies are unable to handle the full load.
The Onboard Administrator manages power allocation rules of various components and can limit
overall power capacity for the enclosure. More information on power management is available in the
technology brief entitled “Managing the HP BladeSystem c-Class”:
http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManual/c00814176/c00814176.pdf.
Dynamic Power Saver mode
In the c3000, the Onboard Administrator module enables Dynamic Power Saver. When enabled, this
feature monitors the total power consumed by the enclosure in real-time and automatically adjusts for
changes in demand. For example, most power supplies operate more efficiently when heavily loaded
and less efficiently when lightly loaded. Dynamic Power Saver mode shifts power load for maximum
power supply efficiency and reliability. Maximizing power supply efficiency reduces operating costs.
Power supply efficiency is simply a measure of DC watts output divided by AC or DC watts input. At
50 percent efficiency, 2000W input would yield 1000W output. The difference is costly wasted
energy that generates unnecessary heat.
Dynamic Power Saver mode is active by default since it saves power in the majority of situations.
When enabled, Dynamic Power Saver runs the required power supplies at a higher use rate and puts
unneeded power supplies in standby mode. A typical power supply running at 20 percent load could
have an efficiency rating as low as 60 percent. However, at 50 percent load, the efficiency rating
could be up to 90 percent, providing a significant savings in power consumption.
30


















