Technical Description of TANDBERG Gateway with software version G2
D13192 Rev. 02 18
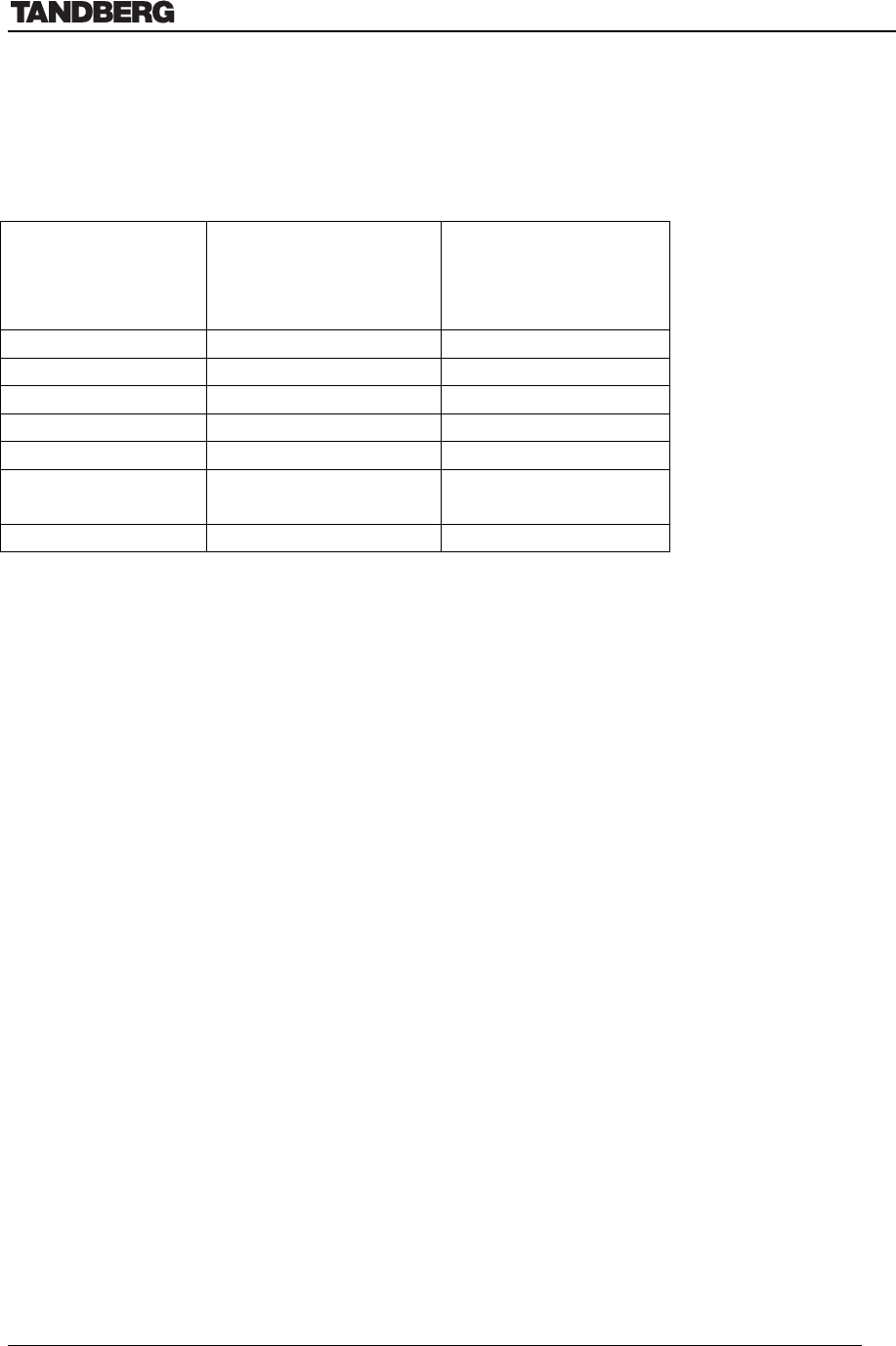
4.1.8.1 TANDBERG Gateway Capacity – typical scenarios for 4Mb Option
In the table below some typical capacity scenarios are listed (they can be derived by the
calculation above):
Bandwidth Non-encrypted
(Max. no. of video
calls + telephone
calls) IP & E1
Encrypted
(Max. no. of video
calls)
128 kbps 8 + 8 7
256 kbps 8 + 7 6
384 kbps 8 + 4 5
512 kbps 7 + 4 5
768 kbps 5 + 0 3
1472 kbps
(1.5Mbps)
2 + 8 N/A
1920 kbps (2Mbps) 2 + 0* N/A
*) Limited by the maximum capacity 7680 kbps, see rule II a) above.
4.1.9 Secure Conference (Encryption)
The TANDBERG Gateway has built-in encryption of audio, video and data for both H.323
(based on ITU standard H.235) and H.320 (based on ITU standard H.233 and H.234).
The encryption algorithms used in the TANDBERG Gateway and all other TANDBERG
systems are:
- The Data Encryption Standard (DES) with a 56 bits session key
- The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) with a 128 bits session key
Although there are small differences between H.323 and H.320, a typical set-up of a secure call
can be defined as follow:
1. Establishement of a common shared secret and selection of a encryption algorithm.
2. Exchange of the keys according to the common shared secret and the selected encryption
algorithm.
3. Start the encryption.
The establishment of the common shared secret is done through the computation of the Diffie-
Hellman (DH) algorithm. The DH method uses primes numbers of 512 bits length for DES and
1024 bits for AES. The shared secret is then used as a key for the selected encryption algorithm


















