ZyXEL G-162/G-360 User’s Guide
WLAN Networking 2-15
Chapter 2
Wireless LAN Networking
This chapter provides background information on general wireless LAN networking technology
and terminology.
2.1 Overview
This section describes the wireless LAN network terms and applications.
2.1.1 SSID
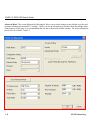
The SSID (Service Set Identity) is a unique name shared among all wireless devices in a wireless network.
Wireless devices must have the same SSID to communicate with each other.
2.1.2 Channel
A radio frequency used by a wireless device is called a channel.
2.1.3 Transmission Rate (Transfer Rate)
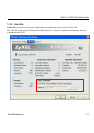
The ZyXEL G-162/G-360 provides various transmission (data) rate options for you to select. Options
include
Fully Auto
,
1 Mbps
,
2 Mbps
,
5.5 Mbps
,
6 Mbps, 11 Mbps
,
9 Mbps
,
12 Mbps
,
18 Mbps
,
22
Mbps
,
24 Mbps
,
36 Mbps
,
48 Mbps and
54 Mbps
and
125Mbps
. In most networking scenarios, the
factory default Fully Auto setting proves the most efficient. This setting allows your ZyXEL G-162/G-360
to operate at the maximum transmission (data) rate. When the communication quality drops below a certain
level, the ZyXEL G-162/G-360 automatically switches to a lower transmission (data) rate. Transmission at
lower data speeds is usually more reliable. However, when the communication quality improves again, the
ZyXEL G-162/G-360 gradually increases the transmission (data) rate again until it reaches the highest
available transmission rate.
2.1.4 Wireless Network Application
Wireless LAN works in either of the two modes: ad-hoc and infrastructure.
To connect to a wired network within a coverage area using Access Points (APs), set the ZyXEL G-162/G-
360 operation mode to Infrastructure (BSS). An AP acts as a bridge between the wireless stations and the
wired network. In case you do not wish to connect to a wired network, but prefer to set up a small
independent wireless workgroup without an AP, use the
Ad-hoc (IBSS)
(Independent Basic Service Set)
mode.