M-302 User’s Guide
Appendix C 75
For added security, certificate-based authentications (EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS and PEAP) use
dynamic keys for data encryption. They are often deployed in corporate environments, but for
public deployment, a simple user name and password pair is more practical. The following
table is a comparison of the features of authentication types.
WPA
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is a subset of the IEEE 802.11i standard.
Key differences between WPA and WEP are improved data encryption and user
authentication.
Select WEP only when the AP and/or wireless clients do not support WPA. WEP is less secure
than WPA.
Encryption
WPA improves data encryption by using Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP), Message
Integrity Check (MIC) and IEEE 802.1x. WPA uses Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) in
the Counter mode with Cipher block chaining Message authentication code Protocol (CCMP)
to offer stronger encryption than TKIP.
TKIP uses 128-bit keys that are dynamically generated and distributed by the authentication
server. AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is a block cipher that uses a 256-bit
mathematical algorithm called Rijndael. They both include a per-packet key mixing function,
a Message Integrity Check (MIC) named Michael, an extended initialization vector (IV) with
sequencing rules, and a re-keying mechanism.
WPA regularly changes and rotate the encryption keys so that the same encryption key is never
used twice.
The RADIUS server distributes a Pairwise Master Key (PMK) key to the AP that then sets up
a key hierarchy and management system, using the PMK to dynamically generate unique data
encryption keys to encrypt every data packet that is wirelessly communicated between the AP
and the wireless stations. This all happens in the background automatically.
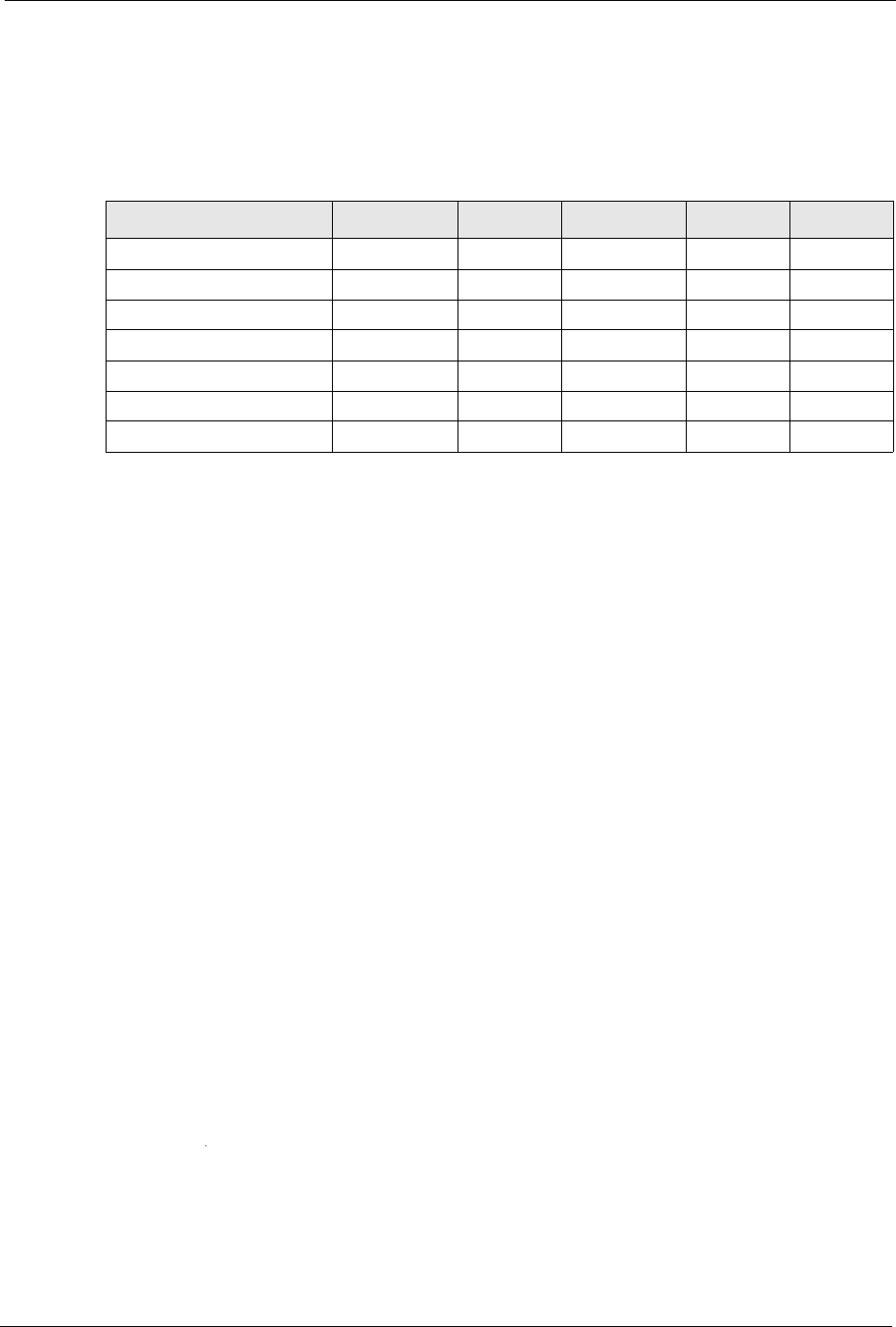
Table 29 Comparison of EAP Authentication Types
EAP-MD5 EAP-TLS EAP-TTLS PEAP LEAP
Mutual Authentication No Yes Yes Yes Yes
Certificate – Client No Yes Optional Optional No
Certificate – Server No Yes Yes Yes No
Dynamic Key Exchange No Yes Yes Yes Yes
Credential Integrity None Strong Strong Strong Moderate
Deployment Difficulty Easy Hard Moderate Moderate Moderate
Client Identity Protection No No Yes Yes No


















