Page 48 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: IGMP
Static IGMP > Example
Static IGMP
Static IGMP enables you to configure a switch with specified group-to-interface or group-to-
port mappings, which you may want to do if:
z your network includes hosts that cannot send IGMP Membership Reports
z you need to guarantee that a specific multicast stream is instantly available on a port,
without any delay from the joining process
A common usage of Static IGMP is for protocols like Service Location Protocol (SLP). This
protocol sends out multicast packets that need to be forwarded to designated ports. You may
want SLP packets to be forwarded to ports that have servers who need to respond to these
packets. Static IGMP allows you to specify that traffic for this group should go to hosts who
will respond to, or are interested in, these messages. For detailed information about using
Static IGMP and SLP, see How to configure IGMP snooping with unregistered multicast addresses
such as Service Location Protocol (SLP) in the Allied Telesis website’s Technical Library.
Static IGMP is available on all the Allied Telesis managed layer 3 switches listed on page 3.
Example
In this example, we will start by setting an IGMP static entry for the group 224.
1
2.
1
3.
1
4 to go
to port 5 on switch
1
(part of vlan
1
00). On that port we have attached a host which has no
multicast client software running. After examining the effect of static IGMP on switch
1
, we
will add a static IGMP entry to switch 3 and consider the effect this has on multicasting
through the network.
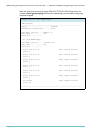
The network for this example has three switches in a loop and is shown in the following
figure.
AT-8948
Switch 1:
Querier
Rapier 24i
Switch 2:
Snooper
Rapier 24i
Switch 3
Static client
(added later in example)
port 5
port 5
port 25 port 25
port 26 port 26
port 50
(blocked by STP)
port 49
Multicast Server
port 1
Static client
igmp-static.eps