ELECTRONIC TANDEM NETWORK (ETN) THROUGH THE ETN AND PNA PACKAGES 5-7
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
Note that a System 75 or Generic 1 communications system that functions as a tandem supports only a 7-
digit uniform numbering plan; while DIMENSION, System 85, and Generic 2 communications systems
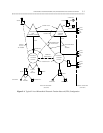
support a 5-, 6-, or 7-digit uniform numbering plan. An example of a private network with a uniform
numbering plan is shown in figure 5-3.
Note: Uniform numbering does not necessary imply uniform dialing at every switch in the network. The
dialing plan is implemented through the administration of the internal dial plan, and not through AAR
administration. The numbers callers dial to reach a particular ETN destination depend upon the following
variables:
• The type of switch where the call originates
• The function the switch plays in the MS/T-ETN complex
• The networking software running on the switch
• Switch administration
For how these variables affect the dialing plan among the main, satellite, tributary, and tandem switches,
see the Routing Incoming Calls and Routing Outgoing Calls sections of chapter 4. To identify the call for
other tandems, a tandem switch always sends the location code (RNX) and the extension number as it
routes the call to the next tandem in the ETN.
Automatic Alternate Routing
Automatic Alternate Routing (AAR) is the feature that routes calls using the private network numbering
plan. Chapter 2 describes AAR processing and administration.
Automatic Route Selection
Automatic Route Selection (ARS) is the feature that routes calls using the North American numbering plan
(NPA-NXX-XXXX). Chapter 2 describes ARS processing and administration.
ETN INTERACTIONS WITH OTHER NETWORKS
The software and administration that lets a switch function as a node in an ETN also allows it to interact
with the following types of networks:
• Extension number portability clusters
• Software-Defined Networks
• Release link trunk networks
• Distributed communications system clusters
• Main-satellite/tributary networks