9-6 DATA COMMUNICATIONS CONFIGURATIONS
_ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
_ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
_ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
CONNECTIONS THROUGH PUBLIC OR PRIVATE DATA NETWORKS
You can connect your local communications systems with each other through DS1 facilities over public or
private data networks for file transfers, video teleconferencing, image processing, and FAX transmittal.
Connecting the sites through a DS1 facility allows you to take full advantage of the DS1 capacity — for
multiple data applications, or for both voice and data.
File Transfers
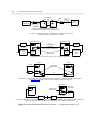
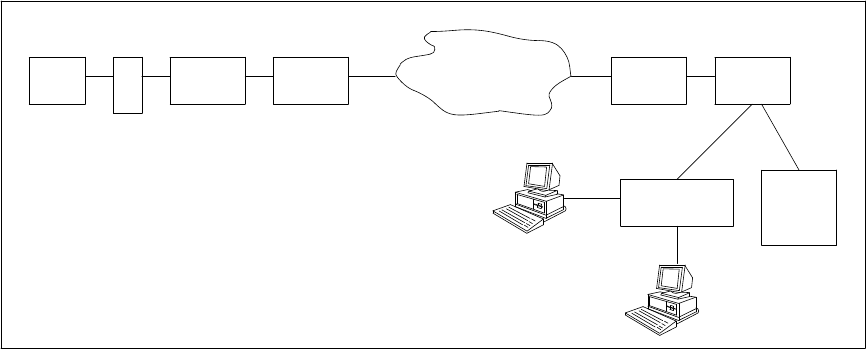
Figure 9-3 shows a possible configuration for the transfer of data from one communications system site to
another. Any AT&T nodal service (for example, the ACCUNET Switched Digital Service, ACCUNET T1.5,
ACCUNET Spectrum, ACCUNET Packet Service, and so forth) can be used in the transfer. To use the packet
network, however, the data must be processed by an X.25 packet assembler/disassembler (see chapter 8)
immediately before and after it is processed through the network. File transfer applications include bulk
data transfer, database update transactions, and electronic messaging.
CLUSTER
CONTROLLER
MPDM
MPDM
S75/S85/
G1/G2
S75/S85/
G1/G2
F
E
P
HOST
IBM
DATA NETWORK
DS1 DS1
IBM SYS.
36/38
43XX;
NON-IBM
. . . OR . . .
Figure 9-3. A Possible File-Transfer Configuration
Video Teleconferencing
Slow-scan video teleconferencing between communications system sites is possible via a single or double
56-kbps DS1 connection. For example, PICTURETEL has made it possible to transmit full-motion video
over the SW56 and SW64 capabilities of the ACCUNET Switched Digital Service or the Software-Defined
Digital Network. The recommended configuration for this type of connection is shown in figure 9-4.