Billion 800VGT Router
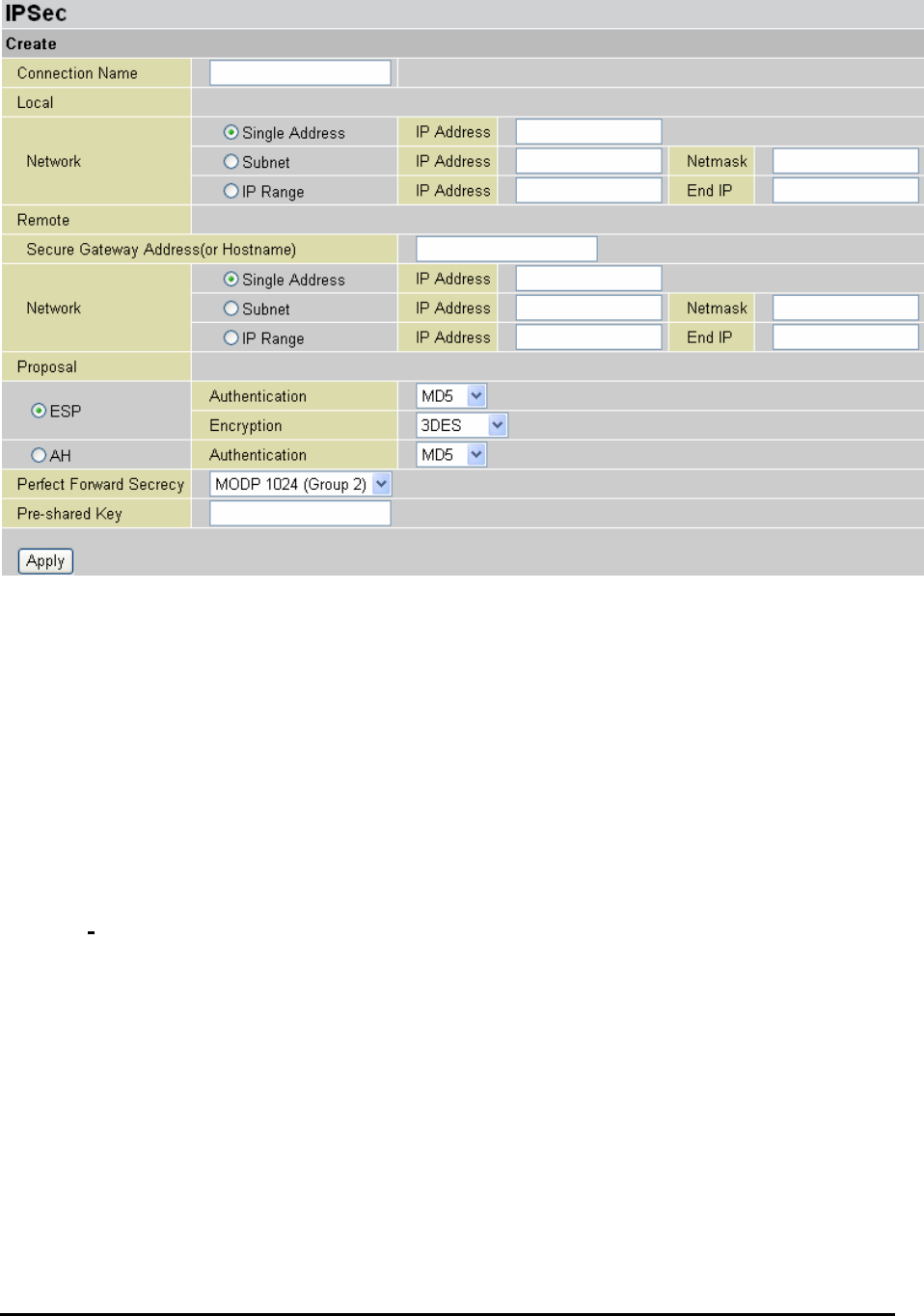
IPSec
VPN
Connection
Connection
Name:
The
user-defined
name
for
the
connection
(e.g.
“connection
to
office”).
Local
Network:
Set
the
IP
address,
subnet
or
address
range
of
the
local
network.
Single
Address:
The
IP
address
of
the
local
host.
Subnet:
The
subnet
of
the
local
network.
For
example,
IP:
192.168.1.0
with
netmask
255.255.255.0
specifies
one
class
C
subnet
starting
from
192.168.1.1
(i.e.
192.168.1.1
through
to
192.168.1.254).
IP
Range:
The
IP
address
range
of
the
local
network.
For
example,
IP:
192.168.1.1,
end
IP:
192.168.1.10.
Remote
Secure
Gateway
Address
(or
Domain
Name):
The
IP
address
or
hostname
of
the
remote
VPN
device
that
is
to
be
connected
to
when
establishing
a
VPN
tunnel.
Remote
Network:
Set
the
IP
address,
subnet
or
address
range
of
the
remote
network.
Proposal:
Select
the
IPSec
security
method.
There
are
two
methods
of
checking
the
authentication
information,
AH
(authentication
header)
and
ESP
(Encapsulating
Security
Payload).
Use
ESP
for
greater
security
so
that
data
will
be
encrypted
and
authenticated.
Using
AH
data
will
be
authenticated
but
not
encrypted.
Authentication:
Authentication
establishes
the
integrity
of
the
datagram
and
ensures
it
is
not
tampered
with
during
transmission.
There
are
three
options,
Message
Digest
5
(
MD5
),
Secure
Hash
Algorithm
(
SHA1
)
or
NONE
.
SHA1
is
more
resistant
to
brute-force
attacks
than
MD5,
however
it
is
slower.
MD5:
A
one-way
hashing
algorithm
that
produces
a
128−bit
hash.
SHA1:
A
one-way
hashing
algorithm
that
produces
a
160−bit
hash.
Encryption:
Select
the
encryption
method
from
the
pull-down
menu.
There
are
several
options,
DES
,
3DES
,
AES
(128,
192
and
256)
and
NULL
.
NULL
means
it
is
a
tunnel
only
with
no
encryption.
3DES
and
AES
are
more
powerful
but
increase
latency.
DES:
Stands
for
Data
Encryption
Standard,
it
uses
56
bits
as
an
encryption
method.
79
Chapter
4:
Configuration


















