20020601
English
2-12-1
Activity: SetupActivity: Setup
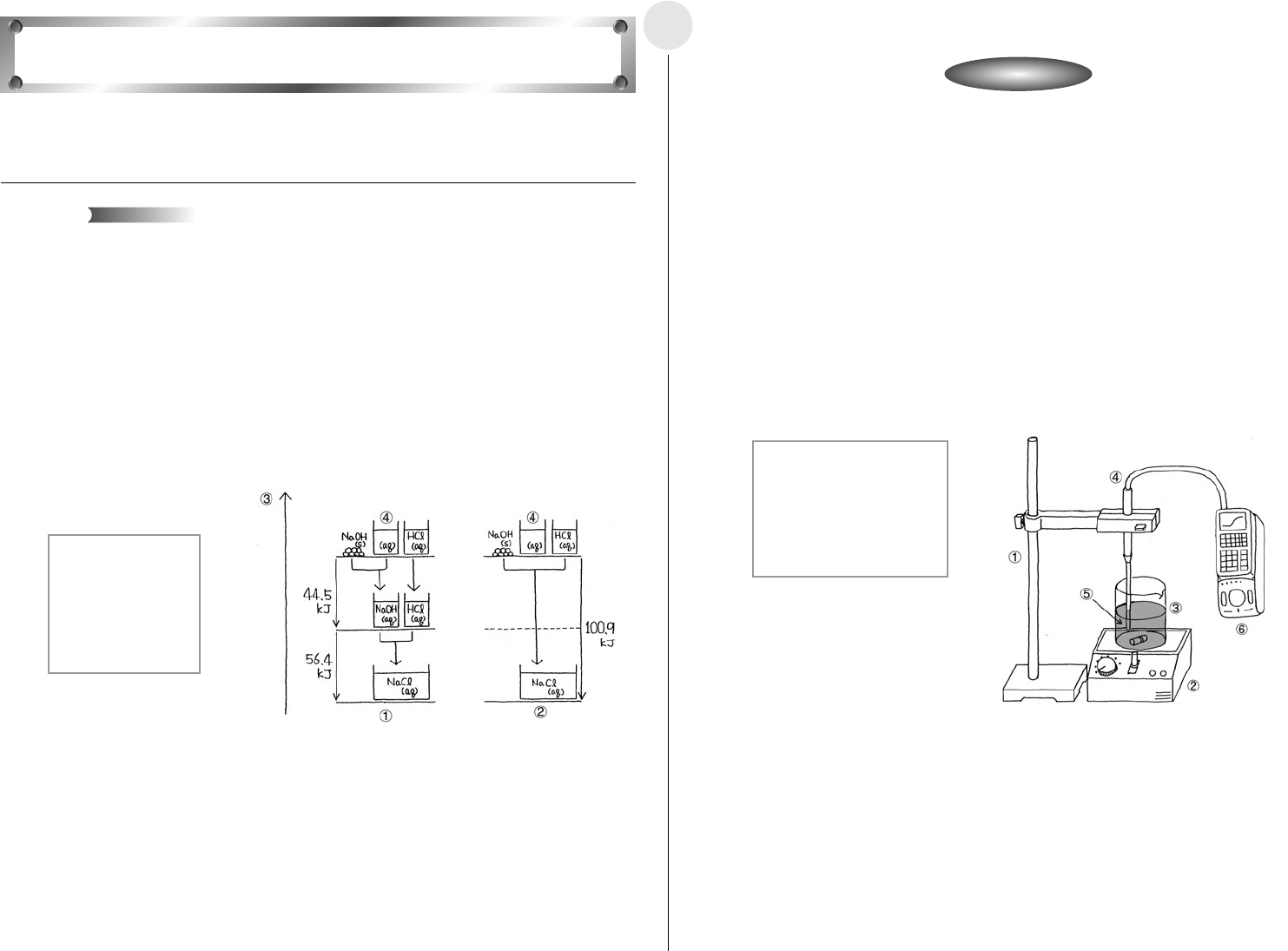
í Equipment
Stand Auto Stirrer Beaker (3)
Hydrochloric Acid (Solution) Sodium Hydroxide (Solid) Distilled Water
Temperature Measurement Setup (EA-200, graphic scientific calculator,
data communication cable, temperature probe)
í Setting Up
u Measure the mass of the hydrochloric acid (aq) and distilled water to be used in the
activity.
u Measure the amount of sodium hydroxide (s) required so the number of its moles is equal
to that of the hydrochloric acid (
aq).
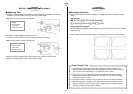
u Fix the probe in place at a point between the center of the beaker and the wall of the
beaker, in a location where it does not strike the stirrer’s magnet, at a depth so it is
sufficiently immersed in the solution.
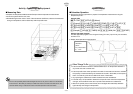
This activity uses the neutralization of hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide to study heat
that is given off or absorbed by chemical reactions.
A chemical reaction causes a change in the properties of matter, and always gives off or
absorbs heat. The sum of the heat of reaction when a chemical reaction takes place
depends solely on the condition of the matter at the time of the reaction, and is totally
independent of the reaction pathway and the number of steps between the initial state and
the final state. This is called Hess’s law.
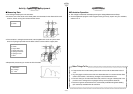
The following illustrates the chemical reaction when sodium chloride (
aq) is generated from
sodium hydroxide (
s) and hydrochloric acid (aq).
Here, Reaction Path 1 includes the heat of dissolution when sodium hydroxide (
s) is
dissolved in distilled water, and the heat of neutralization of sodium hydroxide (
aq) and
hydrochloric acid (
aq).
Reaction Path 2, on the other hand, consists of the heat of neutralization of sodium
hydroxide (
s) and hydrochloric acid (aq).
All of this means that the total heat is the same, regardless of whether or not the pathway
includes a process for dissolving the sodium hydroxide (
s), as in Reaction Path 1.
Exothermic Reaction
Theory
1 Stand
2 Auto Stirrer
3 Beaker
4 Te mperature Probe (CH1)
5 Solution
6 EA-200
1 Reaction Path 1
2 Reaction Path 2
3 Energy
4 Solvent (Water)
s:solid
aq:aqua
NaOH(s)
+ aq = NaOH(aq) + 44.5kJ
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) = NaCl(aq) + H
2
O + 56.4kJ
NaOH(s) + HCl(aq) = NaCl(aq) + H
2
O + 100.9kJ