E-29
k Converting an Input Value to the
Calculator’s Default Angle Unit
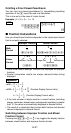
After inputting a value, press 1G(DRG') to display the angle
unit specification menu shown below. Press the number key that
corresponds to the angle unit of the input value. The calculator will
automatically convert it to the calculator’s default angle unit.
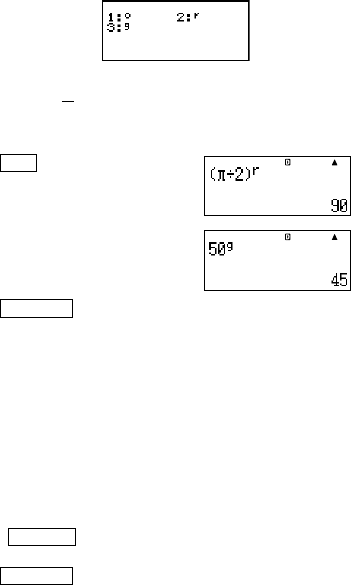
Example: To convert the following values to degrees:
radians = 90°, 50 grads = 45°
The following procedure assumes that the calculator’s default angle
unit is degrees.
LINE
(15(π)/2)
1G(DRG')2(
r
)=
501G(DRG')
3(
g
)=
Appendix
<#018> cos (π radians) = –1, cos (100 grads) = 0
<#019> cos
–1
(–1) = 180
cos
–1
(–1) = π
k Exponential Functions and Logarithmic
Functions
•For the logarithmic function “log(”, you can specify base m using
the syntax “log (m, n)”.
If you input only a single value, a base of 10 is used for the
calculation.
• “ln(” is a natural logarithm function with base e.
•You can also use the & key when inputting an expression with
the form of “logmn” while using Math format. For details, see
Appendix <#020>. Note that you must input the base (base m)
when using the & key for input.
Appendix <#021> to <#023>
*1 A base of 10 (common logarithm) is used if no base is specified.
π
2