E-47
4. Prefix symbol: (–) (negative sign)
5. Statistical estimated value calculation: m, n, m1, m2
6. Permutations, combinations: nPr, nCr
7. Multiplication and division: ×, ÷
Multiplication where sign is omitted: Multiplication sign omitted immediately
before π, e, variables (2π, 5A, πA, etc.), functions with parentheses (2'(3),
Asin(30), etc.)
8. Addition and subtraction: +, –
If a calculation contains a negative value, you may need to enclose the negative
value in parentheses. If you want to square the value –2, for example, you need to
input: (–2)
2
. This is because x
2
is a function preceded by a value (Priority 2,
above), whose priority is greater than the negative sign, which is a prefix symbol
(Priority 4).
Example:
y2w= –2
2
= –4
(y2)w= (–2)
2
= 4
Multiplication and division, and multiplication where the sign is omitted are the
same priority (Priority 7), so these operations are performed from left to right
when both types are mixed in the same calculation. Enclosing an operation within
parentheses causes it to be performed first, so the use of parentheses can result
in different calculation results.
Example:
1/215(π)= 1 ÷ 2π = 1.570796327
1/(215(π))= 1 ÷ (2π) = 0.1591549431
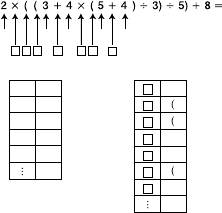
k Stack Limitations
This calculator uses memory areas called
stacks
to temporarily store lower
calculation priority sequence values, commands, and functions. The
numeric stack
has 10 levels and the
command stack
has 24 levels, as shown in the illustration
below.
A Stack ERROR occurs when the calculation you are performing causes the
capacity of either stack to be exceeded.
1
2
3
45
1 2 3 4 5 6
7
Numeric Stack Command Stack
҂
ѿ
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
2
3
4
4
5
5
4
҂
ѿ
5
6
7


















