Note: If AP Group VLANs are configured, and an IGMP join is sent from a client through the controller, it is
placed on the default VLAN of the WLAN that the client is on. Therefore, the client might not receive this
multicast traffic unless the client is a member of this default broadcast domain.
Multicast−Multicast Delivery Method
The multicast−multicast delivery method does not require the controller to replicate each multicast packet
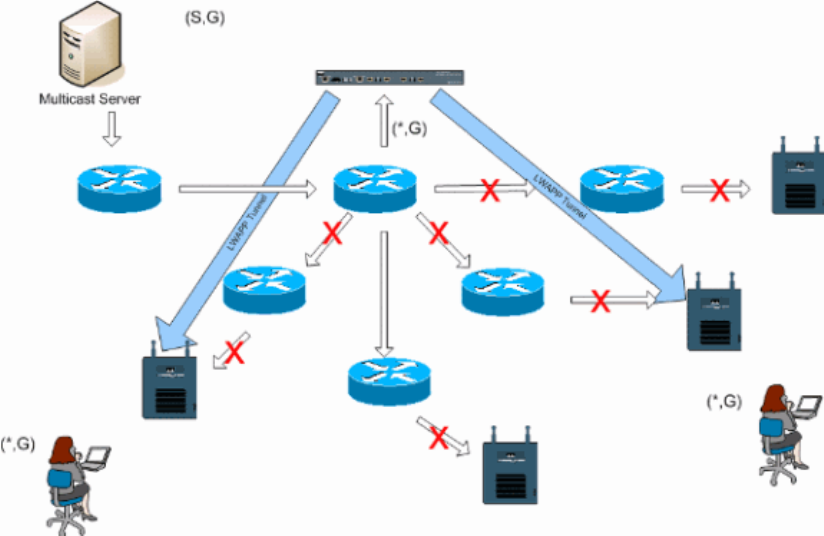
received. The controller is configured for an un−used multicast group address that each access point becomes
a member of. With Figure 3, the multicast group defined from the WLC to the access point is 239.0.0.65.
When a client sends a multicast join to the WLAN, the access point forwards this join through the LWAPP
tunnel to the controller. The controller forwards this link−layer protocol onto it's directly connected local area
network connection that is the default VLAN for the associated WLAN of the client. The router that is local to
the controller then adds this multicast group address to that interface for forwarding ((*,G)) entry. With Figure
3, the example multicast join was sent to the multicast group 239.0.0.30. When the network now forwards
multicast traffic, the multicast address of 239.0.0.30 is forwarded to the controller. The controller then
encapsulates the multicast packet into an LWAPP multicast packet addressed to the multicast group address
(example here is 239.0.0.65) that is configured on the controller and forwarded to the network. Each access
point on the controller receives this packet as a member of the controllers multicast group. The access point
then forwards the clients/servers multicast packet (example here is 239.0.0.30) as a broadcast to the
WLAN/SSID identified within the LWAPP multicast packet.
Note: If you improperly configure your multicast network, you could end up receiving another controller's
access point multicast packets. If the first controller has to fragment this multicast packet, the fragment is
forwarded to the network and each access point must spend time to drop this fragment. If you allow all traffic
such as anything from the 224.0.0.x multicast range, this is also encapsulated and subsequently forwarded by
each access point.
Figure 3LWAPP Multicast−Multicast


















